Search results for: Heat Treatment
2021 Comparison of the Effects of Continuous Flow Microwave Pre-treatment with Different Intensities on the Anaerobic Digestion of Sewage Sludge for Sustainable Energy Recovery from Sewage Treatment Plant
Authors: D. Hephzibah, P. Kumaran, N. M. Saifuddin
Abstract:
Anaerobic digestion is a well-known technique for sustainable energy recovery from sewage sludge. However, sewage sludge digestion is restricted due to certain factors. Pre-treatment methods have been established in various publications as a promising technique to improve the digestibility of the sewage sludge and to enhance the biogas generated which can be used for energy recovery. In this study, continuous flow microwave (MW) pre-treatment with different intensities were compared by using 5 L semi-continuous digesters at a hydraulic retention time of 27 days. We focused on the effects of MW at different intensities on the sludge solubilization, sludge digestibility, and biogas production of the untreated and MW pre-treated sludge. The MW pre-treatment demonstrated an increase in the ratio of soluble chemical oxygen demand to total chemical oxygen demand (sCOD/tCOD) and volatile fatty acid (VFA) concentration. Besides that, the total volatile solid (TVS) removal efficiency and tCOD removal efficiency also increased during the digestion of the MW pre-treated sewage sludge compared to the untreated sewage sludge. Furthermore, the biogas yield also subsequently increases due to the pre-treatment effect. A higher MW power level and irradiation time generally enhanced the biogas generation which has potential for sustainable energy recovery from sewage treatment plant. However, the net energy balance tabulation shows that the MW pre-treatment leads to negative net energy production.
Keywords: Anaerobic digestion, biogas, microwave pre-treatment, sewage sludge.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 21472020 Conjugate Heat Transfer in an Enclosure Containing a Polygon Object
Authors: Habibis Saleh, Ishak Hashim
Abstract:
Conjugate natural convection in a differentially heated square enclosure containing a polygon shaped object is studied numerically in this article. The effect of various polygon types on the fluid flow and thermal performance of the enclosure is addressed for different thermal conductivities. The governing equations are modeled and solved numerically using the built-in finite element method of COMSOL software. It is found that the heat transfer rate remains stable by varying the polygon types.Keywords: Natural convection, Polygon object, COMSOL
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 18902019 Fin Spacing Effect of the Tube Fin Heat Exchanger at the Floor Heating Convector
Authors: F. Lemfeld, K. Frana
Abstract:
This article deals with numerical simulation of the floor heating convector in 3D. Numerical simulation is focused on cooling mode of the floor heating convector. Geometrical model represents section of the heat exchanger – two fins with the gap between, pipes are not involved. Two types of fin are examined – sinusoidal and angular shape with different fin spacing. Results of fin spacing in case of constant Reynolds number are presented. For the numerical simulation was used commercial software Ansys Fluent.Keywords: fin spacing, cooling output, floor heating convector, numerical simulation.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 19622018 Contaminant Transport Modeling Due to Thermal Diffusion Effects with the Effect of Biodegradation
Authors: Nirmala P. Ratchagar, S. Senthamilselvi
Abstract:
The heat and mass transfer characteristics of contaminants in groundwater subjected to a biodegradation reaction is analyzed by taking into account the thermal diffusion (Soret) effects. This phenomenon is modulated mathematically by a system of partial differential equations which govern the motion of fluid (groundwater) and solid (contaminants) particles. The numerical results are presented graphically for different values of the parameters entering into the problem on the velocity profiles of fluid, contaminants, temperature and concentration profile.Keywords: Heat and mass transfer, Soret number, porous media.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 16232017 Wear Regimes of Al-Cu-Mg Matrix Composites
Authors: R. N. Rao, S. L. Tulasi Devi
Abstract:
Tribological behavior and wear regimes of ascast and heattreted Al-Cu-Mg matrix composites containing SiC particles were studied using a pin-on-disc wear testing apparatus against an EN32 steel counterface giving emphasis on wear rate as a function of applied pressures (0.2, 0.6, 1.0 and 1.4 MPa) at different sliding distances (1000, 2000, 3000, 4000 and 5000 meters) and at a fixed sliding speed of 3.35m/s. The results showed that the composite exhibited lower wear rate than that of the matrix alloy and the wear rate of the composites is noted to be invariant to the sliding distance and is reducing by heat treatment. Wear regimes such as low, mild and severe wear were observed as per the Archard-s wear calculations. It is very interesting to note that the mild wear is almost constant in all the wear regimes.Keywords: Aluminum, matrix, regimes, wear.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 20902016 Photovoltaic Small-Scale Wastewater Treatment Project for Rural and New-Cultivated Areas in Egypt
Authors: Fadia M. A. Ghali
Abstract:
The problem of wastewater treatment in Egypt is a two-fold problem; the first part concerning the existing rural areas, the second one dealing with new industrial/domestic areas. In Egypt several agricultural projects have been initiated by the government and the private sector as well, in order to change its infrastructure. As a reliable energy source, photovoltaic pumping systems have contributed to supply water for local rural communities worldwide; they can also be implemented to solve the problem “wastewater environment pollution". The solution of this problem can be categorised as recycle process. In addition, because of regional conditions past technologies are being reexamined to select a smallscale treatment system requiring low construction and maintenance costs. This paper gives the design guidelines of a Photovoltaic Small- Scale Wastewater Treatment Plant (PVSSWTP) based on technologies that can be transferred.
Keywords: Renewable energy sources, Photovoltaic, small-scale projects, wastewater treatment.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 26022015 Treatment of Oily Wastewater by Fibrous Coalescer Process: Stage Coalescer and Model Prediction
Authors: Pisut Painmanakul, Kotchakorn Kongkangwarn, Nattawin Chawaloesphonsiya
Abstract:
The coalescer process is one of the methods for oily water treatment by increasing the oil droplet size in order to enhance the separating velocity and thus effective separation. However, the presence of surfactants in an oily emulsion can limit the obtained mechanisms due to the small oil size related with stabilized emulsion. In this regard, the purpose of this research is to improve the efficiency of the coalescer process for treating the stabilized emulsion. The effects of bed types, bed height, liquid flow rate and stage coalescer (step-bed) on the treatment efficiencies in term of COD values were studied. Note that the treatment efficiency obtained experimentally was estimated by using the COD values and oil droplet size distribution. The study has shown that the plastic media has more effective to attach with oil particles than the stainless one due to their hydrophobic properties. Furthermore, the suitable bed height (3.5 cm) and step bed (3.5 cm with 2 steps) were necessary in order to well obtain the coalescer performance. The application of step bed coalescer process in reactor has provided the higher treatment efficiencies in term of COD removal than those obtained with classical process. The proposed model for predicting the area under curve and thus treatment efficiency, based on the single collector efficiency (ηT) and the attachment efficiency (α), provides relatively a good coincidence between the experimental and predicted values of treatment efficiencies in this study.
Keywords: Stage coalescer, stabilized emulsions, treatment efficiency, model prediction.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 21982014 Energy Absorption and Axial Tearing Behaviour of Metallic Tubes Using Angled Dies: Experimental and Numerical Simulation
Authors: V. K. Bheemineni, B. Käfer, H. Lammer, M. Kotnik, F. O. Riemelmoser
Abstract:
This paper concerns about the experimental and numerical investigations of energy absorption and axial tearing behaviour of aluminium 6060 circular thin walled tubes under static axial compression. The tubes are received in T66 heat treatment condition with fixed outer diameter of 42mm, thickness of 1.5mm and length of 120mm. The primary variables are the conical die angles (15°, 20° and 25°). Numerical simulations are carried on ANSYS/LS-DYNA software tool, for investigating the effect of friction between the tube and the die.
Keywords: Angled die, ANSYS/LS-DYNA, Axial tearing, Energy absorption.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 25602013 Thermodynamic Analysis of Activated Carbon- CO2 based Adsorption Cooling Cycles
Authors: Skander Jribi, Anutosh Chakraborty, Ibrahim I. El-Sharkawy, Bidyut Baran Saha, Shigeru Koyama
Abstract:
Heat powered solid sorption is a feasible alternative to electrical vapor compression refrigeration systems. In this paper, activated carbon (powder type Maxsorb and fiber type ACF-A10)- CO2 based adsorption cooling cycles are studied using the pressuretemperature- concentration (P-T-W) diagram. The specific cooling effect (SCE) and the coefficient of performance (COP) of these two cooling systems are simulated for the driving heat source temperatures ranging from 30 ºC to 90 ºC in terms of different cooling load temperatures with a cooling source temperature of 25 ºC. It is found from the present analysis that Maxsorb-CO2 couple shows higher cooling capacity and COP. The maximum COPs of Maxsorb-CO2 and ACF(A10)-CO2 based cooling systems are found to be 0.15 and 0.083, respectively. The main innovative feature of this cooling cycle is the ability to utilize low temperature waste heat or solar energy using CO2 as the refrigerant, which is one of the best alternative for applications where flammability and toxicity are not allowed.Keywords: Activated carbon, Adsorption cooling system, Carbon dioxide, Performance evaluation.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 36822012 Numerical Solutions of Boundary Layer Flow over an Exponentially Stretching/Shrinking Sheet with Generalized Slip Velocity
Authors: Ezad Hafidz Hafidzuddin, Roslinda Nazar, Norihan M. Arifin, Ioan Pop
Abstract:
In this paper, the problem of steady laminar boundary layer flow and heat transfer over a permeable exponentially stretching/shrinking sheet with generalized slip velocity is considered. The similarity transformations are used to transform the governing nonlinear partial differential equations to a system of nonlinear ordinary differential equations. The transformed equations are then solved numerically using the bvp4c function in MATLAB. Dual solutions are found for a certain range of the suction and stretching/shrinking parameters. The effects of the suction parameter, stretching/shrinking parameter, velocity slip parameter, critical shear rate and Prandtl number on the skin friction and heat transfer coefficients as well as the velocity and temperature profiles are presented and discussed.
Keywords: Boundary Layer, Exponentially Stretching/Shrinking Sheet, Generalized Slip, Heat Transfer, Numerical Solutions.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 27022011 MHD Chemically Reacting Viscous Fluid Flow towards a Vertical Surface with Slip and Convective Boundary Conditions
Authors: Ibrahim Yakubu Seini, Oluwole Daniel Makinde
Abstract:
MHD chemically reacting viscous fluid flow towards a vertical surface with slip and convective boundary conditions has been conducted. The temperature and the chemical species concentration of the surface and the velocity of the external flow are assumed to vary linearly with the distance from the vertical surface. The governing differential equations are modeled and transformed into systems of ordinary differential equations, which are then solved numerically by a shooting method. The effects of various parameters on the heat and mass transfer characteristics are discussed. Graphical results are presented for the velocity, temperature, and concentration profiles whilst the skin-friction coefficient and the rate of heat and mass transfers near the surface are presented in tables and discussed. The results revealed that increasing the strength of the magnetic field increases the skin-friction coefficient and the rate of heat and mass transfers toward the surface. The velocity profiles are increased towards the surface due to the presence of the Lorenz force, which attracts the fluid particles near the surface. The rate of chemical reaction is seen to decrease the concentration boundary layer near the surface due to the destructive chemical reaction occurring near the surface.Keywords: Boundary layer, surface slip, MHD flow, chemical reaction, heat transfer, mass transfer.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 22402010 Bio-Electrochemical Process Coupled with MnO2 Nanowires for Wastewater Treatment
Authors: A. Giwa, S. M. Jung, W. Fang, J. Kong, S. W. Hasan
Abstract:
MnO2 nanowires were developed as filtration media for wastewater treatment that uniquely combines several advantages. The resulting material demonstrated strong capability to remove the pollution of heavy metal ions and organic contents in water. In addition, the manufacture process of such material is practical and economical. In this work, MnO2 nanowires were integrated with the state-of-art bio-electrochemical system for wastewater treatment, to overcome problems currently encountered with organic, inorganic, heavy metal, and microbe removal, and to minimize the unit footprint (land/space occupation) at low cost. Results showed that coupling the bio-electrochemical with MnO2 resulted in very encouraging results with higher removal efficiencies of such pollutants.
Keywords: Bio-electrochemical, nanowires, wastewater, treatment.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 12722009 Effect of Helium-Argon Mixtures on the Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow in Gas Tungsten Arc Welding
Authors: A. Traidia, F. Roger, A. Chidley, J. Schroeder, T. Marlaud
Abstract:
A transient finite element model has been developed to study the heat transfer and fluid flow during spot Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW) on stainless steel. Temperature field, fluid velocity and electromagnetic fields are computed inside the cathode, arc-plasma and anode using a unified MHD formulation. The developed model is then used to study the influence of different helium-argon gas mixtures on both the energy transferred to the workpiece and the time evolution of the weld pool dimensions. It is found that the addition of helium to argon increases the heat flux density on the weld axis by a factor that can reach 6.5. This induces an increase in the weld pool depth by a factor of 3. It is also found that the addition of only 10% of argon to helium decreases considerably the weld pool depth, which is due to the electrical conductivity of the mixture that increases significantly when argon is added to helium.Keywords: GTAW, Thermal plasmas, Fluid flow, Marangoni effect, Shielding Gases.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 32342008 Investigation on Some Ergonomics and Psychological Strains of Common Militarism Protective Clothing
Authors: A. Ashjaran, A. Rashidi, R. Ghazi-Saeidi
Abstract:
Protective clothing limits heat transfer and hampers task performance due to the increased weight. Militarism protective clothing enables humans to operate in adverse environments. In the selection and evaluation of militarism protective clothing attention should be given to heat strain, ergonomic and fit issues next to the actual protection it offers. Fifty Male healthy subjects participated in the study. The subjects were dressed in shorts, T-shirts, socks, sneakers and four deferent kinds of militarism protective clothing such as CS, CSB, CS with NBC protection and CS with NBC- protection added. Ergonomically and psychological strains of every four cloths were investigated on subjects by walking on a treadmill (7km/hour) with a 19.7 kg backpack. As a result of these tests were showed that, the highest heart rate was found wearing the NBC-protection added outfit, the highest temperatures were observed wearing NBCprotection added, followed by respectively CS with NBC protection, CSB and CS and the highest value for thermal comfort (implying worst thermal comfort) was observed wearing NBC-protection added.Keywords: Militarist protective clothing, Ergonomic, Heat strain, Thermal comfort
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 16562007 Grape Seed Extract in Prevention and Treatment of Liver Toxic Cirrhosis in Rats
Authors: S. Buloyan, V. Mamikonyan, H. Hakobyan, H. Harutyunyan, H. Gasparyan
Abstract:
The liver is the strongest regenerating organ of the organism, and even with 2/3 surgically removed, it can regenerate completely. Hence liver cirrhosis may only develop when the regenerating system is off. We present the results of a comparative study of structural and functional characteristics of rat liver tissue under the conditions of toxic liver cirrhosis development, induced by carbon tetrachloride, and its prevention/treatment by natural compounds with antioxidant and immune stimulating action. Studies were made on Wister rats, weighing 120~140 g. Grape seeds extracts, separately and in combination with well-known anticirrhotic drug ursodeoxycholic acid (Urdoxa), have demonstrated effectiveness in prevention of liver cirrhosis development and its treatment.
Keywords: Carbon tetrachloride, GSE, liver cirrhosis, prevention, treatment.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 37462006 A Previously Underappreciated Impact on Global Warming caused by the Geometrical and Physical Properties of desert sand
Authors: Y. F. Yang, B. T. Wang, J. J. Fan, J. Yin
Abstract:
The previous researches focused on the influence of anthropogenic greenhouse gases exerting global warming, but not consider whether desert sand may warm the planet, this could be improved by accounting for sand's physical and geometric properties. Here we show, sand particles (because of their geometry) at the desert surface form an extended surface of up to 1 + π/4 times the planar area of the desert that can contact sunlight, and at shallow depths of the desert form another extended surface of at least 1 + π times the planar area that can contact air. Based on this feature, an enhanced heat exchange system between sunlight, desert sand, and air in the spaces between sand particles could be built up automatically, which can increase capture of solar energy, leading to rapid heating of the sand particles, and then the heating of sand particles will dramatically heat the air between sand particles. The thermodynamics of deserts may thus have contributed to global warming, especially significant to future global warming if the current desertification continues to expand.Keywords: global warming, desert sand, extended surface, heat exchange, thermodynamics
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 16332005 Effect of Viscous Dissipation and Axial Conduction in Thermally Developing Region of the Channel Partially Filled with a Porous Material Subjected to Constant Wall Heat Flux
Authors: D Bhargavi, J. Sharath Kumar Reddy
Abstract:
The present investigation has been undertaken to assess the effect of viscous dissipation and axial conduction on forced convection heat transfer in the entrance region of a parallel plate channel with the porous insert attached to both walls of the channel. The flow field is unidirectional. Flow in the porous region corresponds to Darcy-Brinkman model and the clear fluid region to that of plane Poiseuille flow. The effects of the parameters Darcy number, Da, Peclet number, Pe, Brinkman number, Br and a porous fraction γp on the local heat transfer coefficient are analyzed graphically. Effects of viscous dissipation employing the Darcy model and the clear fluid compatible model have been studied.
Keywords: Porous material, channel partially filled with a porous material, axial conduction, viscous dissipation.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 6402004 Simulation of Thermal Storage Phase Change Material in Buildings
Authors: Samira Haghshenaskashani, Hadi Pasdarshahri
Abstract:
One of the potential and effective ways of storing thermal energy in buildings is the integration of brick with phase change materials (PCMs). This paper presents a two-dimensional model for simulating and analyzing of PCM in order to minimize energy consumption in the buildings. The numerical approach has been used with the real weather data of a selected city of Iran (Tehran). Two kinds of brick integrated PCM are investigated and compared base on outdoor weather conditions and the amount of energy consumption. The results show a significant reduction in maximum entering heat flux to building about 32.8% depending on PCM quantity. The results are analyzed by various temperature contour plots. The contour plots illustrated the time dependent mechanism of entering heat flux for a brick integrated with PCM. Further analysis is developed to investigate the effect of PCM location on the inlet heat flux. The results demonstrated that to achieve maximum performance of PCM it is better to locate PCM near the outdoor.Keywords: Building, Energy Storage, PCM, Phase Change Material
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 21892003 Morphological and Electrical Characterization of Polyacrylonitrile Nanofibers Synthesized Using Electrospinning Method for Electrical Application
Authors: Divyanka Sontakke, Arpit Thakre, D. K Shinde, Sujata Parmeshwaran
Abstract:
Electrospinning is the most widely utilized method to create nanofibers because of the direct setup, the capacity to mass-deliver consistent nanofibers from different polymers, and the ability to produce ultrathin fibers with controllable diameters. Smooth and much arranged ultrafine Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) nanofibers with diameters going from submicron to nanometer were delivered utilizing Electrospinning technique. PAN powder was used as a precursor to prepare the solution utilized as a part of this process. At the point when the electrostatic repulsion contradicted surface tension, a charged stream of polymer solution was shot out from the head of the spinneret and along these lines ultrathin nonwoven fibers were created. The effect of electrospinning parameter such as applied voltage, feed rate, concentration of polymer solution and tip to collector distance on the morphology of electrospun PAN nanofibers were investigated. The nanofibers were heat treated for carbonization to examine the changes in properties and composition to make for electrical application. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) was performed before and after carbonization to study electrical conductivity and morphological characterization. The SEM images have shown the uniform fiber diameter and no beads formation. The average diameter of the PAN fiber observed 365nm and 280nm for flat plat and rotating drum collector respectively. The four probe strategy was utilized to inspect the electrical conductivity of the nanofibers and the electrical conductivity is significantly improved with increase in oxidation temperature exposed.
Keywords: Electrospinning, polyacrylonitrile carbon nanofibres, heat treatment, electrical conductivity.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 6892002 Second-Order Slip Flow and Heat Transfer in a Long Isoflux Microchannel
Authors: Huei Chu Weng
Abstract:
This paper presents a study on the effect of second-order slip on forced convection through a long isoflux heated or cooled planar microchannel. The fully developed solutions of flow and thermal fields are analytically obtained on the basis of the second-order Maxwell-Burnett slip and local heat flux boundary conditions. Results reveal that when the average flow velocity increases or the wall heat flux amount decreases, the role of thermal creep becomes more insignificant, while the effect of second-order slip becomes larger. The second-order term in the Deissler slip boundary condition is found to contribute a positive velocity slip and then to lead to a lower pressure drop as well as a lower temperature rise for the heated-wall case or to a higher temperature rise for the cooled-wall case. These findings are contrary to predictions made by the Karniadakis slip model.
Keywords: Microfluidics, forced convection, thermal creep, second-order boundary conditions.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 23582001 Heat and Mass Transfer Modelling of Industrial Sludge Drying at Different Pressures and Temperatures
Authors: L. Al Ahmad, C. Latrille, D. Hainos, D. Blanc, M. Clausse
Abstract:
A two-dimensional finite volume axisymmetric model is developed to predict the simultaneous heat and mass transfers during the drying of industrial sludge. The simulations were run using COMSOL-Multiphysics 3.5a. The input parameters of the numerical model were acquired from a preliminary experimental work. Results permit to establish correlations describing the evolution of the various parameters as a function of the drying temperature and the sludge water content. The selection and coupling of the equation are validated based on the drying kinetics acquired experimentally at a temperature range of 45-65 °C and absolute pressure range of 200-1000 mbar. The model, incorporating the heat and mass transfer mechanisms at different operating conditions, shows simulated values of temperature and water content. Simulated results are found concordant with the experimental values, only at the first and last drying stages where sludge shrinkage is insignificant. Simulated and experimental results show that sludge drying is favored at high temperatures and low pressure. As experimentally observed, the drying time is reduced by 68% for drying at 65 °C compared to 45 °C under 1 atm. At 65 °C, a 200-mbar absolute pressure vacuum leads to an additional reduction in drying time estimated by 61%. However, the drying rate is underestimated in the intermediate stage. This rate underestimation could be improved in the model by considering the shrinkage phenomena that occurs during sludge drying.
Keywords: Industrial sludge drying, heat transfer, mass transfer, mathematical modelling.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 6712000 Field Emission Properties of Multi-wall Carbon Nanotube Field Emitters using Graphite Tip by Electroporetic Deposition
Authors: Gui Sob Byun, Yang Doo Lee, Kyong Soo Lee, Keun Soo Lee, Sun-Woo Park, Byeong Kwon Ju
Abstract:
We fabricated multi-walled carbon nanotube (MCNT) emitters by an electroporetic deposition (EPD) method using a MCNT-sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) suspension. MCNT films were prepared on graphite tip using EPD. We observe field emission properties of MCNT film after heat treatment. Consequently, The MCNT film on graphite tip exhibit good electron emission current.Keywords: Field emission, Multi-wall carbon-nanotube (MCNT), Electrophoretic deposition (EPD)
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 14141999 Potential Role of Halophytic Macrophytes in Saline Effluent Treatment
Authors: R. Hegedűs, É. Kerepeczki, D. Gál, F. Pekár, M. Oncsik Bíróné, Gy. Lakatos
Abstract:
The growth of the aquaculture industry has been associated with negative environmental impacts through the discharge of raw effluents into the adjacent receiving water bodies. Macrophytes from natural saline lakes, which have adaptability to the high salinity, can be suitable for saline effluent treatment. Eight emergent species from natural saline area were planted in an experimental gravel bed hydroponic mesocosm (GBH) which was treated with effluent water from an intensive fish farm using geothermal water. In order to examine the applicability of the halophytes in treatment processes, we tested the relative efficacy of total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), potassium (K), sodium (Na), magnesium (Mg) and calcium (Ca) removal for the saline wastewater treatment. Four of the eight species, which were Phragmites australis, Typha angustifolia, Glyceria maxima, Scirpus lacustris spp. tabernaemontani could survive and contribute the experimental treatment.Keywords: Gravel bed hydroponic system, halophytes, intensive fish farm, salt removal
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 21511998 Temperature Evolution, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Heat-Treatable Aluminum Alloy Welded by Friction Stir Welding: Comparison with Tungsten Inert Gas
Authors: Saliha Gachi, Mouloud Aissani, Fouad Boubenider
Abstract:
Friction Stir Welding (FSW) is a solid-state welding technique that can join material without melting the plates to be welded. In this work, we are interested to demonstrate the potentiality of FSW for joining the heat-treatable aluminum alloy 2024-T3 which is reputed as difficult to be welded by fusion techniques. Thereafter, the FSW joint is compared with another one obtained from a conventional fusion process Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG). FSW welds are made up using an FSW tool mounted on a milling machine. Single pass welding was applied to fabricated TIG joint. The comparison between the two processes has been made on the temperature evolution, mechanical and microstructure behavior. The microstructural examination revealed that FSW weld is composed of four zones: Base metal (BM), Heat affected zone (HAZ), Thermo-mechanical affected zone (THAZ) and the nugget zone (NZ). The NZ exhibits a recrystallized equiaxed refined grains that induce better mechanical properties and good ductility compared to TIG joint where the grains have a larger size in the welded region compared with the BM due to the elevated heat input. The microhardness results show that, in FSW weld, the THAZ contains the lowest microhardness values and increase in the NZ; however, in TIG process, the lowest values are localized on the NZ.
Keywords: Friction stir welding, tungsten inert gaz, aluminum, microstructure.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 7821997 Two Dimensional Simulation of Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer in the Transition Flow Regime using a Lattice Boltzmann Approach
Authors: Mehdi Shamshiri, Mahmud Ashrafizaadeh
Abstract:
The significant effects of the interactions between the system boundaries and the near wall molecules in miniaturized gaseous devices lead to the formation of the Knudsen layer in which the Navier-Stokes-Fourier (NSF) equations fail to predict the correct associated phenomena. In this paper, the well-known lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) is employed to simulate the fluid flow and heat transfer processes in rarefied gaseous micro media. Persuaded by the problematic deficiency of the LBM in capturing the Knudsen layer phenomena, present study tends to concentrate on the effective molecular mean free path concept the main essence of which is to compensate the incapability of this mesoscopic method in dealing with the momentum and energy transport within the above mentioned kinetic boundary layer. The results show qualitative and quantitative accuracy comparable to the solutions of the linearized Boltzmann equation or the DSMC data for the Knudsen numbers of O (1) .Keywords: Fluid flow and Heat transfer, Knudsen layer, Lattice Boltzmann method (LBM), Micro-scale numerical simulation, Transition regime.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 17631996 Microstructure and Aging Behavior of Nonflammable AZ91D Mg Alloy
Authors: Seok Hong Min, Tae Kwon Ha
Abstract:
Phase equilibria of AZ91D Mg alloys for nonflammable use, containing Ca and Y, were carried out by using FactSage® and FTLite database, which revealed that solid solution treatment could be performed at temperatures from 400 to 450oC. Solid solution treatment of AZ91D Mg alloy without Ca and Y was successfully conducted at 420oC and supersaturated microstructure with all beta phase resolved into matrix was obtained. In the case of AZ91D Mg alloy with some Ca and Y; however, a little amount of intermetallic particles were observed after solid solution treatment. After solid solution treatment, each alloy was annealed at temperatures of 180 and 200oC for time intervals from 1 min to 48 hrs and hardness of each condition was measured by micro-Vickers method. Peak aging conditions were deduced as at the temperature of 200oC for 10 hrs.
Keywords: Mg alloy, AZ91D, nonflammable alloy, phase equilibrium, peak aging.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 22361995 MHD Stagnation Point Flow towards a Shrinking Sheet with Suction in an Upper-Convected Maxwell (UCM) Fluid
Authors: K. Jafar, R. Nazar, A. Ishak, I. Pop
Abstract:
The present analysis considers the steady stagnation point flow and heat transfer towards a permeable shrinking sheet in an upper-convected Maxwell (UCM) electrically conducting fluid, with a constant magnetic field applied in the transverse direction to flow and a local heat generation within the boundary layer, with a heat generation rate proportional to (T-T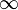 )p Using a similarity transformation, the governing system of partial differential equations is first transformed into a system of ordinary differential equations, which is then solved numerically using a finite-difference scheme known as the Keller-box method. Numerical results are obtained for the flow and thermal fields for various values of the stretching/shrinking parameter λ, the magnetic parameter M, the elastic parameter K, the Prandtl number Pr, the suction parameter s, the heat generation parameter Q, and the exponent p. The results indicate the existence of dual solutions for the shrinking sheet up to a critical value λc whose value depends on the value of M, K, and s. In the presence of internal heat absorption (Q<0) the surface heat transfer rate decreases with increasing p but increases with parameters Q and s when the sheet is either stretched or shrunk.
)p Using a similarity transformation, the governing system of partial differential equations is first transformed into a system of ordinary differential equations, which is then solved numerically using a finite-difference scheme known as the Keller-box method. Numerical results are obtained for the flow and thermal fields for various values of the stretching/shrinking parameter λ, the magnetic parameter M, the elastic parameter K, the Prandtl number Pr, the suction parameter s, the heat generation parameter Q, and the exponent p. The results indicate the existence of dual solutions for the shrinking sheet up to a critical value λc whose value depends on the value of M, K, and s. In the presence of internal heat absorption (Q<0) the surface heat transfer rate decreases with increasing p but increases with parameters Q and s when the sheet is either stretched or shrunk.
Keywords: Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD), boundary layer flow, UCM fluid, stagnation point, shrinking sheet.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 20711994 Coaxial Helix Antenna for Microwave Coagulation Therapy in Liver Tissue Simulations
Authors: M. Chaichanyut, S. Tungjitkusolmun
Abstract:
This paper is concerned with microwave (MW) ablation for a liver cancer tissue by using helix antenna. The antenna structure supports the propagation of microwave energy at 2.45 GHz. A 1½ turn spiral catheter-based microwave antenna applicator has been developed. We utilize the three-dimensional finite element method (3D FEM) simulation to analyze where the tissue heat flux, lesion pattern and volume destruction during MW ablation. The configurations of helix antenna where Helix air-core antenna and Helix Dielectric-core antenna. The 3D FEMs solutions were based on Maxwell and bio-heat equations. The simulation protocol was power control (10 W, 300s). Our simulation result, both helix antennas have heat flux occurred around the helix antenna and that can be induced the temperature distribution similar (teardrop). The region where the temperature exceeds 50°C the microwave ablation was successful (i.e. complete destruction). The Helix air-core antenna and Helix Dielectric-core antenna, ablation zone or axial ratios (Widest/length) were respectively 0.82 and 0.85; the complete destructions were respectively 4.18 cm3 and 5.64 cm3Keywords: Liver cancer, Helix antenna, Finite element, Microwave ablation.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 19601993 Mixed Convection Boundary Layer Flows Induced by a Permeable Continuous Surface Stretched with Prescribed Skin Friction
Authors: Mohamed Ali
Abstract:
The boundary layer flow and heat transfer on a stretched surface moving with prescribed skin friction is studied for permeable surface. The surface temperature is assumed to vary inversely with the vertical direction x for n = -1. The skin friction at the surface scales as (x-1/2) at m = 0. The constants m and n are the indices of the power law velocity and temperature exponent respectively. Similarity solutions are obtained for the boundary layer equations subject to power law temperature and velocity variation. The effect of various governing parameters, such as the buoyancy parameter λ and the suction/injection parameter fw for air (Pr = 0.72) are studied. The choice of n and m ensures that the used similarity solutions are x independent. The results show that, assisting flow (λ > 0) enhancing the heat transfer coefficient along the surface for any constant value of fw. Furthermore, injection increases the heat transfer coefficient but suction reduces it at constant λ.Keywords: Stretching surface, Boundary layers, Prescribed skin friction, Suction or injection, similarity solutions, buoyancy effects.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 18561992 Conceptual Solution and Thermal Analysis of the Final Cooling Process of Biscuits in Factory "Jaffa" at Crvenka, in Serbia
Authors: Duško Salemović, Aleksandar Dedić, Matilda Lazić, Dragan Halas
Abstract:
The paper presents the conceptual solution for the final cooling of the chocolate dressing of biscuit in one confectionary factory in Serbia. The proposed concept solution was derived from the desired technological process of final cooling of biscuit and the required process parameters that were to be achieved, and which were an integral part of the project task. The desired process parameters for achieving proper hardening and coating formation are: the exchanged amount of heat in the time unit between the two media (air and chocolate dressing), speed of air inside the tunnel cooler and the surface of all biscuits in contact with the air. These parameters were calculated in the paper. The final cooling of chocolate dressing on biscuits could be optimized by changing process parameters and dimensions of the tunnel cooler, and looking for the appropriate values for them. The accurate temperature predictions and fluid flow analysis could be conducted by using heat balance and flow balance equations having in mind theory of similarity. Furthermore, some parameters were adopted from previous technology process, such as: inlet temperature of biscuits and input air temperature. A thermal calculation was carried out and it was demonstrated that the percentage error between the contact surface of the air and the chocolate biscuit topping, which is obtained from the heat balance and geometrically 0.67%, which is very good agreement. This enabled quality of the cooling process of chocolate dressing applied on biscuit and hardness of its coating.
Keywords: Air, chocolate dressing, cooling, heat balance.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 14