Search results for: Phase change magnetic materials
3689 Visual Study on Flow Patterns and Heat Transfer during Convective Boiling Inside Horizontal Smooth and Microfin Tubes
Authors: V.D. Hatamipour, M.A. Akhavan-Behabadi
Abstract:
Evaporator is an important and widely used heat exchanger in air conditioning and refrigeration industries. Different methods have been used by investigators to increase the heat transfer rates in evaporators. One of the passive techniques to enhance heat transfer coefficient is the application of microfin tubes. The mechanism of heat transfer augmentation in microfin tubes is dependent on the flow regime of two-phase flow. Therefore many investigations of the flow patterns for in-tube evaporation have been reported in literatures. The gravitational force, surface tension and the vapor-liquid interfacial shear stress are known as three dominant factors controlling the vapor and liquid distribution inside the tube. A review of the existing literature reveals that the previous investigations were concerned with the two-phase flow pattern for flow boiling in horizontal tubes [12], [9]. Therefore, the objective of the present investigation is to obtain information about the two-phase flow patterns for evaporation of R-134a inside horizontal smooth and microfin tubes. Also Investigation of heat transfer during flow boiling of R-134a inside horizontal microfin and smooth tube have been carried out experimentally The heat transfer coefficients for annular flow in the smooth tube is shown to agree well with Gungor and Winterton-s correlation [4]. All the flow patterns occurred in the test can be divided into three dominant regimes, i.e., stratified-wavy flow, wavy-annular flow and annular flow. Experimental data are plotted in two kinds of flow maps, i.e., Weber number for the vapor versus weber number for the liquid flow map and mass flux versus vapor quality flow map. The transition from wavy-annular flow to annular or stratified-wavy flow is identified in the flow maps.Keywords: Flow boiling, Flow pattern, Heat transfer, Horizontal, Smooth tube, Microfin tube.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 23303688 Haematology and Serum Biochemical Profile of Laying Chickens Reared on Deep Litter System with or without Access to Grass or Legume Pasture under Humid Tropical Climate
Authors: E. Oke, A. O. Ladokun, J. O. Daramola, O. M. Onagbesan
Abstract:
There has been a growing interest on the effects of access to pasture on poultry health status. However, there is a paucity of data on the relative benefits of grass and legume pastures. An experiment was conducted to determine the effects of rearing systems {deep litter system (DL), deep litter with access to legumes (LP) or grass (GP) pastures} haematology and serum chemistry of ISA Brown layers. The study involved the use of two hundred and forty 12 weeks old pullets. The birds were reared until 60 weeks of age. Eighty birds were assigned to each treatment; each treatment had four replicates of 20 birds each. Blood samples (2.5 ml) were collected from the wing vein of two birds per replicate and serum chemistry and haematological parameters were determined. The results showed that there were no significant differences between treatments in all the parameters considered at 18 weeks of age. At 24 weeks old, the percentage of heterophyl (HET) in DL and LP were similar but higher than that of GP. The ratio of H:L was higher (P<0.05) in DL than those of LP and GP while LP and GP were comparable. At week 38 of age, the percentage of PCV in the birds in LP and GP were similar but the birds in DL had significantly lower level than that of GP. In the early production phase, serum total protein of the birds in LP was similar to that of GP but higher (P<0.05) than that of DL. At the peak production phase (week 38), the total protein in GP and DL were similar but significantly lower than that of LP. The albumin level in LP was greater (P<0.05) than GP but similar to that of DL. In the late production phase, the total protein in LP was significantly higher than that of DL but similar to that of GP. It was concluded that rearing chickens in either grass or legume pasture did not have deleterious effects on the health of laying chickens but improved some parameters including blood protein and HET/lymphocyte.Keywords: Rearing systems, Stylosanthes, Cynodon serum chemistry, haematology, hen.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 20653687 Temperature-dependent Structural Perturbation of Tuna Myoglobin
Authors: Yoshihiro Ochiai
Abstract:
To unveil the mechanism of fast autooxidation of fish myoglobins, the effect of temperature on the structural change of tuna myoglobin was investigated. Purified myoglobin was subjected to preincubation at 5, 20, 50 and 40oC. Overall helical structural decay through thermal treatment up to 95oC was monitored by circular dichroism spectrometry, while the structural changes around the heme pocket was measured by ultraviolet/visible absorption spectrophotometry. As a result, no essential structural change of myoglobin was observed under 30oC, roughly equivalent to their body temperature, but the structure was clearly damaged at 40oC. The Soret band absorption hardly differed irrespective of preincubation temperature, suggesting that the structure around the heme pocket was not perturbed even after thermal treatment.Keywords: denaturation, myoglobin, stability, tuna.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 19853686 Analysis on Spatiotemporal Pattern of Land Surface Temperature in Kunming City, China
Authors: Jinrui Ren, Li Wu
Abstract:
Anthropogenic activities and changes of underlying surface affect the temporal and spatial distribution of surface temperature in Kunming. Taking Kunming city as the research area, the surface temperature in 2000, 2010 and 2020 as the research object, using ENVI 5.3 and ArcGIS 10.8 as auxiliary tools, and based on the spatial autocorrelation method, this paper devoted to exploring the interactions among the changes of surface temperature, urban heat island effect and land use type, so as to provide theoretical basis and scientific basis for mitigating climate change. The results showed that: (1) The heat island effect was obvious in Kunming City, the high temperature area increased from 604 km2 in 2000 to 1269 km2 in 2020, and the sub-high temperature area reached 1099 km2 in 2020; (2) In terms of space, the spatial distribution of LST was significantly different with the change of underlying surface. The high temperature zone extended in three directions: south, north and east. The overall spatial distribution pattern of LST was high in the east and low in the west. (3) The inter-annual fluctuation of land surface temperature (LST) was large, and the growth rate was faster, from 2000 to 2010. The lowest temperature in 2000 was 13.45 ℃, which raised to 19.71 ℃ in 2010, and the temperature difference in 10 years was 6.26 ℃. (4) The land use/land cover type has a strong effect on the change of LST: the man-made land made a great contribution to the increase of LST, followed by grassland and farmland, while forest and water have a significant cooling effect on LST. To sum up, the variation of surface temperature in Kunming is the result of the interactions of human activities and climate change.
Keywords: Surface temperature, urban heat island effect, land use cover type, spatiotemporal variation.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 1873685 Applications of Social Marketing in Road Safety of Georgia
Authors: Charita Jashi
Abstract:
The aim of the paper is to explore the role of social marketing in changing the behavior of consumers on road safety, identify critical aspects and priority needs which impede the implementation of road safety program in Georgia. Given the goals of the study, a quantitative method was used to carry out interviews for primary data collection. This research identified the awareness level of road safety, legislation base, and marketing interventions to change behavior of drivers and pedestrians. During several years the non-governmental sector together with the local authorities and media have been very intensively working on the road safety issue in Georgia, but only seat-belts campaign should be considered rather successful. Despite achievements in this field, efficiency of road safety programs far from fulfillment and needs strong empowering.
Keywords: Road safety, social marketing interventions, behavior change, well-being.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 11153684 Investigating the Fiber Content, Fiber Length, and Curing Characteristics of 3D Printed Recycled Carbon Fiber
Authors: Peng Hao Wang, Ronald Sterkenburg, Garam Kim, Yuwei He
Abstract:
As composite materials continue to gain popularity in the aerospace industry; large airframe sections made out of composite materials are becoming the standard for aerospace manufacturers. However, the heavy utilization of these composite materials also increases the importance of the recycling of these composite materials. A team of Purdue University School of Aviation and Transportation Technology (SATT) faculty and students have partnered to investigate the characteristics of 3D printed recycled carbon fiber. A prototype of a 3D printed recycled carbon fiber part was provided by an industry partner and different sections of the prototype were used to create specimens. A furnace was utilized in order to remove the polymer from the specimens and the specimen’s fiber content and fiber length was calculated from the remaining fibers. A differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) test was also conducted on the 3D printed recycled carbon fiber prototype in order to determine the prototype’s degree of cure at different locations. The data collected from this study provided valuable information in the process improvement and understanding of 3D printed recycled carbon fiber.
Keywords: 3D printed, carbon fiber, fiber content, recycling.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 7683683 Performance of Subcarrier- OCDMA System with Complementary Subtraction Detection Technique
Authors: R. K. Z. Sahbudin, M. K. Abdullah, M. Mokhtar, S. B. A. Anas, S. Hitam
Abstract:
A subcarrier - spectral amplitude coding optical code division multiple access system using the Khazani-Syed code with Complementary subtraction detection technique is proposed. The proposed system has been analyzed by taking into account the effects of phase-induced intensity noise, shot noise, thermal noise and intermodulation distortion noise. The performance of the system has been compared with the spectral amplitude coding optical code division multiple access system using the Hadamard code and the Modified Quadratic Congruence code. The analysis shows that the proposed system can eliminate the multiple access interference using the Complementary subtraction detection technique, and hence improve the overall system performance.Keywords: Complementary subtraction, Khazani-Syed code, multiple access interference, phase-induced intensity noise
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 17433682 Negative Selection as a Means of Discovering Unknown Temporal Patterns
Authors: Wanli Ma, Dat Tran, Dharmendra Sharma
Abstract:
The temporal nature of negative selection is an under exploited area. In a negative selection system, newly generated antibodies go through a maturing phase, and the survivors of the phase then wait to be activated by the incoming antigens after certain number of matches. These without having enough matches will age and die, while these with enough matches (i.e., being activated) will become active detectors. A currently active detector may also age and die if it cannot find any match in a pre-defined (lengthy) period of time. Therefore, what matters in a negative selection system is the dynamics of the involved parties in the current time window, not the whole time duration, which may be up to eternity. This property has the potential to define the uniqueness of negative selection in comparison with the other approaches. On the other hand, a negative selection system is only trained with “normal" data samples. It has to learn and discover unknown “abnormal" data patterns on the fly by itself. Consequently, it is more appreciate to utilize negation selection as a system for pattern discovery and recognition rather than just pattern recognition. In this paper, we study the potential of using negative selection in discovering unknown temporal patterns.
Keywords: Artificial Immune Systems, ComputationalIntelligence, Negative Selection, Pattern Discovery.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 16653681 Development of a Nano-Alumina-Zirconia Composite Catalyst as an Active Thin Film in Biodiesel Production
Authors: N. Marzban, J. K. Heydarzadeh M. Pourmohammadbagher, M. H. Hatami, A. Samia
Abstract:
A nano-alumina-zirconia composite catalyst was synthesized by a simple aqueous sol-gel method using AlCl3.6H2O and ZrCl4 as precursors. Thermal decomposition of the precursor and subsequent formation of γ-Al2O3 and t-Zr were investigated by thermal analysis. XRD analysis showed that γ-Al2O3 and t-ZrO2 phases were formed at 700 °C. FT-IR analysis also indicated that the phase transition to γ-Al2O3 occurred in corroboration with X-ray studies. TEM analysis of the calcined powder revealed that spherical particles were in the range of 8-12 nm. The nano-alumina-zirconia composite particles were mesoporous and uniformly distributed in their crystalline phase. In order to measure the catalytic activity, esterification reaction was carried out. Biodiesel, as a renewable fuel, was formed in a continuous packed column reactor. Free fatty acid (FFA) was esterified with ethanol in a heterogeneous catalytic reactor. It was found that the synthesized γ-Al2O3/ZrO2 composite had the potential to be used as a heterogeneous base catalyst for biodiesel production processes.Keywords: Nano-alumina-zirconia, composite catalyst, thin film, biodiesel.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 17483680 Human Walking Vertical Force and Vertical Vibration of Pedestrian Bridge Induced by Its Higher Components
Authors: M. Yoneda
Abstract:
The purpose of this study is to identify human walking vertical force by using FFT power spectrum density from the experimental acceleration data of the human body. An experiment on human walking is carried out on a stationary floor especially paying attention to higher components of dynamic vertical walking force. Based on measured acceleration data of the human lumbar part, not only in-phase component with frequency of 2fw, 3fw, but also in-opposite-phase component with frequency of 0.5 fw, 1.5 fw, 2.5 fw where fw is the walking rate is observed. The vertical vibration of pedestrian bridge induced by higher components of human walking vertical force is also discussed in this paper. A full scale measurement for the existing pedestrian bridge with center span length of 33 m is carried out focusing on the resonance phenomenon due to higher components of human walking vertical force. Dynamic response characteristics excited by these vertical higher components of human walking are revealed from the dynamic design viewpoint of pedestrian bridge.
Keywords: Simplified method, Human walking vertical force, Higher component, Pedestrian bridge vibration.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 18163679 Ideal Disinfectant Characteristics According Data in Published Literature
Authors: Saimir Heta, Ilma Robo, Rialda Xhizdari, Kers Kapaj
Abstract:
The stability of an ideal disinfectant should be constant regardless of the change in the atmospheric conditions of the environment where it is kept. If the conditions such as temperature or humidity change, it is understood that it will also be necessary to approach possible changes in the holding materials such as plastic or glass bottles with the aim of protecting the disinfectant, for example, from the excessive lighting of the environment, which can also be translated as an increase in the temperature of disinfectant as a fluid. In this study, an attempt was made to find the most recent published data about the best possible combination of disinfectants indicated for use after dental procedures. This purpose of the study was realized by comparing the basic literature that is studied in the field of dentistry by students with the most published data in the literature of recent years about this topic. Each disinfectant is represented by a number called the disinfectant count, in which different factors can influence the increase or reduction of variables whose production remains a specific statistic for a specific disinfectant. The changes in the atmospheric conditions where the disinfectant is deposited and stored in the environment are known to affect the stability of the disinfectant as a fluid; this fact is known and even cited in the leaflets accompanying the manufactured boxes of disinfectants. It is these cares, in the form of advice, which are based not only on the preservation of the disinfectant but also on the application in order to have the desired clinical result. Aldehydes have the highest constant among the types of disinfectants, followed by acids. The lowest value of the constant belongs to the class of glycols, the predecessors of which were the halogens, in which class there are some representatives with disinfection applications. The class of phenols and acids have almost the same intervals of constants. If the goal were to find the ideal disinfectant among the large variety of disinfectants produced, a good starting point would be to find something unchanging or a fixed, unchanging element on the basis of which the comparison can be made properties of different disinfectants. Precisely based on the results of this study, the role of the specific constant according to the specific disinfectant is highlighted. Finding an ideal disinfectant, like finding a medication or the ideal antibiotic, is an ongoing but unattainable goal.
Keywords: Different disinfectants, phenols, aldehydes, specific constant, dental procedures.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 433678 Synthesizing CuFe2O4 Spinel Powders by a Combustion-Like Process for Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Interconnect Coatings
Authors: S. N. Hosseini, M. H. Enayati, F. Karimzadeh, N. M. Sammes
Abstract:
The synthesis of CuFe2O4 spinel powders by an optimized combustion-like process followed by calcination is described herein. The samples were characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), differential thermal analysis (TG/DTA), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), dilatometry and 4-probe DC methods. Different glycine to nitrate (G/N) ratios of 1 (fuel-deficient), 1.48 (stoichiometric) and 2 (fuel-rich) were employed. Calcining the asprepared powders at 800 and 1000°C for 5 hours showed that the G/N ratio of 2 results in the formation of the desired copper spinel single phase at both calcination temperatures. For G/N=1, formation of CuFe2O4 takes place in three steps. First, iron and copper nitrates decompose to iron oxide and pure copper. Then, copper transforms to copper oxide and finally, copper and iron oxides react with each other to form a copper ferrite spinel phase. The electrical conductivity and the coefficient of thermal expansion of the sintered pelletized samples were 2 S.cm-1 (800°C) and 11×10-6 °C-1 (25-800°C), respectively.Keywords: SOFC interconnect coatings, Copper ferrite, Spinels, Electrical conductivity, Glycine–nitrate process.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 24843677 Pattern Recognition Using Feature Based Die-Map Clusteringin the Semiconductor Manufacturing Process
Authors: Seung Hwan Park, Cheng-Sool Park, Jun Seok Kim, Youngji Yoo, Daewoong An, Jun-Geol Baek
Abstract:
Depending on the big data analysis becomes important, yield prediction using data from the semiconductor process is essential. In general, yield prediction and analysis of the causes of the failure are closely related. The purpose of this study is to analyze pattern affects the final test results using a die map based clustering. Many researches have been conducted using die data from the semiconductor test process. However, analysis has limitation as the test data is less directly related to the final test results. Therefore, this study proposes a framework for analysis through clustering using more detailed data than existing die data. This study consists of three phases. In the first phase, die map is created through fail bit data in each sub-area of die. In the second phase, clustering using map data is performed. And the third stage is to find patterns that affect final test result. Finally, the proposed three steps are applied to actual industrial data and experimental results showed the potential field application.
Keywords: Die-Map Clustering, Feature Extraction, Pattern Recognition, Semiconductor Manufacturing Process.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 31513676 The Potential of Natural Waste (Corn Husk) for Production of Environmental Friendly Biodegradable Film for Seedling
Authors: M. Z. Norashikin, M. Z. Ibrahim
Abstract:
The use of plastic materials in agriculture causes serious hazards to the environment. The introduction of biodegradable materials, which can be disposed directly into the soil can be one possible solution to this problem. In the present research results of experimental tests carried out on biodegradable film fabricated from natural waste (corn husk) are presented. The film was characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), differential scanning calorimeter (DSC), thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA) and atomic force microscope (AFM) observation. The film is shown to be readily degraded within 7-9 months under controlled soil conditions, indicating a high biodegradability rate. The film fabricated was use to produce biodegradable pot (BioPot) for seedlings plantation. The introduction and the expanding use of biodegradable materials represent a really promising alternative for enhancing sustainable and environmentally friendly agricultural activities.Keywords: Environment, waste, plastic, biodegradable.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 50033675 Estimating the Absorption of Volatile Organic Compounds in Four Biodiesels Using the UNIFAC Procedure
Authors: Corina M Mateescu, Edison Muzenda, Mohamed Belaid, Saka Abdulkareem, Ayo S Afolabi
Abstract:
This work considered the thermodynamic feasibility of scrubbing volatile organic compounds into biodiesel in view of designing a gas treatment process with this absorbent. A detailed vapour – liquid equilibrium investigation was performed using the original UNIFAC group contribution method. The four biodiesels studied in this work are methyl oleate, methyl palmitate, methyl linolenate and ethyl stearate. The original UNIFAC procedure was used to estimate the infinite dilution activity coefficients of 13 selected volatile organic compounds in the biodiesels. The calculations were done at the VOC mole fraction of 9.213x10-8. Ethyl stearate gave the most favourable phase equilibrium. A close agreement was found between the infinite dilution activity coefficient of toluene found in this work and those reported in literature. Thermodynamic models can efficiently be used to calculate vast amount of phase equilibrium behaviour using limited number of experimental data.Keywords: Biodiesel, Equilibrium, Gas treatment, Infinitedilution, Thermodynamic
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 18823674 Saving Energy through Scalable Architecture
Authors: John Lamb, Robert Epstein, Vasundhara L. Bhupathi, Sanjeev Kumar Marimekala
Abstract:
In this paper, we focus on the importance of scalable architecture for data centers and buildings in general to help an enterprise achieve environmental sustainability. The scalable architecture helps in many ways, such as adaptability to the business and user requirements, promotes high availability and disaster recovery solutions that are cost effective and low maintenance. The scalable architecture also plays a vital role in three core areas of sustainability: economy, environment, and social, which are also known as the 3 pillars of a sustainability model. If the architecture is scalable, it has many advantages. A few examples are that scalable architecture helps businesses and industries to adapt to changing technology, drive innovation, promote platform independence, and build resilience against natural disasters. Most importantly, having a scalable architecture helps industries bring in cost-effective measures for energy consumption, reduce wastage, increase productivity, and enable a robust environment. It also helps in the reduction of carbon emissions with advanced monitoring and metering capabilities. Scalable architectures help in reducing waste by optimizing the designs to utilize materials efficiently, minimize resources, decrease carbon footprints by using low-impact materials that are environmentally friendly. In this paper we also emphasize the importance of cultural shift towards the reuse and recycling of natural resources for a balanced ecosystem and maintain a circular economy. Also, since all of us are involved in the use of computers, much of the scalable architecture we have studied is related to data centers.
Keywords: Scalable Architectures, Sustainability, Application Design, Disruptive Technology, Machine Learning, Natural Language Processing, AI, Social Media Platform, Cloud Computing, Advanced Networking, Storage Devices, Advanced Monitoring, Metering Infrastructure, Climate change.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 633673 Phase Error Accumulation Methodology for On-Chip Cell Characterization
Authors: Chang Soo Kang, In Ho Im, Sergey Churayev, Timour Paltashev
Abstract:
This paper describes the design of new method of propagation delay measurement in micro and nanostructures during characterization of ASIC standard library cell. Providing more accuracy timing information about library cell to the design team we can improve a quality of timing analysis inside of ASIC design flow process. Also, this information could be very useful for semiconductor foundry team to make correction in technology process. By comparison of the propagation delay in the CMOS element and result of analog SPICE simulation. It was implemented as digital IP core for semiconductor manufacturing process. Specialized method helps to observe the propagation time delay in one element of the standard-cell library with up-to picoseconds accuracy and less. Thus, the special useful solutions for VLSI schematic to parameters extraction, basic cell layout verification, design simulation and verification are announced.Keywords: phase error accumulation methodology, gatepropagation delay, Processor Testing, MEMS Testing
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 14993672 Determination of Material Properties for Biodegradable Polylactic Acid Plastic Used in 3D Printers
Authors: Juraj Beniak, Ľubomír Šooš, Peter Križan, Miloš Matúš
Abstract:
Within Rapid Prototyping technologies are used many types of materials. Many of them are recyclable but there are still as plastic like, so practically they do not degrade in the landfill. Polylactic acid (PLA) is one of the special plastic materials, which are biodegradable and available for 3D printing within Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) technology. The question is, if the mechanical properties of produced models are comparable to similar technical plastic materials which are usual for prototype production. Presented paper shows the experiments results for tensile strength measurements for specimens prepared with different 3D printer settings and model orientation. Paper contains also the comparison of tensile strength values with values measured on specimens produced by conventional technologies as injection moulding.Keywords: 3D printing, biodegradable plastic, fused deposition modeling, PLA plastic, rapid prototyping.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 19443671 Efficient System for Speech Recognition using General Regression Neural Network
Authors: Abderrahmane Amrouche, Jean Michel Rouvaen
Abstract:
In this paper we present an efficient system for independent speaker speech recognition based on neural network approach. The proposed architecture comprises two phases: a preprocessing phase which consists in segmental normalization and features extraction and a classification phase which uses neural networks based on nonparametric density estimation namely the general regression neural network (GRNN). The relative performances of the proposed model are compared to the similar recognition systems based on the Multilayer Perceptron (MLP), the Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) and the well known Discrete Hidden Markov Model (HMM-VQ) that we have achieved also. Experimental results obtained with Arabic digits have shown that the use of nonparametric density estimation with an appropriate smoothing factor (spread) improves the generalization power of the neural network. The word error rate (WER) is reduced significantly over the baseline HMM method. GRNN computation is a successful alternative to the other neural network and DHMM.Keywords: Speech Recognition, General Regression NeuralNetwork, Hidden Markov Model, Recurrent Neural Network, ArabicDigits.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 21853670 Issues on Optimizing the Structural Parameters of the Induction Converter
Authors: Marinka K. Baghdasaryan, Siranush M. Muradyan, Avgen A. Gasparyan
Abstract:
Analytical expressions of the current and angular errors, as well as the frequency characteristics of an induction converter describing the relation with its structural parameters, the core and winding characteristics are obtained. Based on estimation of the dependences obtained, a mathematical problem of parametric optimization is formulated which can successfully be used for investigating and diagnosing an induction converter.
Keywords: Induction converters, magnetic circuit material, current and angular errors, frequency response, mathematical formulation, structural parameters.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 15543669 Understanding Physical Activity Behavior of Type 2 Diabetics Using the Theory of Planned Behavior and Structural Equation Modeling
Authors: D. O. Omondi, M. K. Walingo, G. M. Mbagaya, L. O. A. Othuon
Abstract:
Understanding patient factors related to physical activity behavior is important in the management of Type 2 Diabetes. This study applied the Theory of Planned Behavior model to understand physical activity behavior among sampled Type 2 diabetics in Kenya. The study was conducted within the diabetic clinic at Kisii Level 5 Hospital and adopted sequential mixed methods design beginning with qualitative phase and ending with quantitative phase. Qualitative data was analyzed using grounded theory analysis method. Structural equation modeling using maximum likelihood was used to analyze quantitative data. The common fit indices revealed that the theory of planned behavior fitted the data acceptably well among the Type 2 diabetes and within physical activity behavior {¤ç2 = 213, df = 84, n=230, p = .061, ¤ç2/df = 2.53; TLI = .97; CFI =.96; RMSEA (90CI) = .073(.029, .08)}. This theory proved to be useful in understanding physical activity behavior among Type 2 diabetics.
Keywords: Physical activity, Theory of Planned Behavior, Type2 diabetes, Kenya.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 19843668 Application of the Experimental Planning Design to the Notched Precracked Tensile Fracture of Composite
Authors: N. Mahmoudi
Abstract:
Composite materials have important assets compared to traditional materials. They bring many functional advantages: lightness, mechanical resistance and chemical, etc. In the present study we examine the effect of a circular central notch and a precrack on the tensile fracture of two woven composite materials. The tensile tests were applied to a standardized specimen, notched and a precarcked (orientation of the crack 0°, 45° and 90°). These tensile tests were elaborated according to an experimental planning design of the type 23.31 requiring 24 experiments with three repetitions. By the analysis of regression, we obtained a mathematical model describing the maximum load according to the influential parameters (hole diameter, precrack length, angle of a precrack orientation). The specimens precracked at 90° have a better behavior than those having a precrack at 45° and still better than those having of the precracks oriented at 0°. In addition the maximum load is inversely proportional to the notch size.
Keywords: Polymer matrix, Glasses, Fracture.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 18593667 An Improved Prediction Model of Ozone Concentration Time Series Based On Chaotic Approach
Authors: N. Z. A. Hamid, M. S. M. Noorani
Abstract:
This study is focused on the development of prediction models of the Ozone concentration time series. Prediction model is built based on chaotic approach. Firstly, the chaotic nature of the time series is detected by means of phase space plot and the Cao method. Then, the prediction model is built and the local linear approximation method is used for the forecasting purposes. Traditional prediction of autoregressive linear model is also built. Moreover, an improvement in local linear approximation method is also performed. Prediction models are applied to the hourly Ozone time series observed at the benchmark station in Malaysia. Comparison of all models through the calculation of mean absolute error, root mean squared error and correlation coefficient shows that the one with improved prediction method is the best. Thus, chaotic approach is a good approach to be used to develop a prediction model for the Ozone concentration time series.
Keywords: Chaotic approach, phase space, Cao method, local linear approximation method.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 17843666 Harmonic Pollution Control of the Electrical Network by Three-Phase Shunt Active Filter: Comparative Study of Controls, by Hysteresis and by Duty Cycle Modulation
Authors: T. Patrice Nna Nna, S. Ndjakomo Essiane, S. Pérabi Ngoffé, F. Amigue Fissou
Abstract:
This paper deals with the harmonic decontamination of current in an electrical grid by an active shunt filter in order to improve power quality. The contribution of this paper is mainly based on the proposal of a control strategy for an active filter based on Duty Cycle Modulation (DCM). First, three-monophase method is applied for the identification of disturbing currents. A Simulink model of this method is given for one phase of the grid. Secondly, two orders were designed: the first one is the Hysteresis Control and the second one is the DCM Control. Finally, a comparative study of the two controls was performed. The results obtained show a significant improvement in the rate of harmonic distortion for both controls. The harmonic distortion for the Hysteresis control is limited by the non-controllability of the switching frequencies of the inverter's switches and reduces the harmonic distortion rate (THD) to 3.12% as opposed to the DCM control which limits the THD to 2.82% which makes it better.Keywords: Harmonic pollution, shunt active filter, hysteresis, Duty Cycle Modulation.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 6333665 Modeling Directional Thermal Radiance Anisotropy for Urban Canopy
Authors: Limin Zhao, Xingfa Gu, C. Tao Yu
Abstract:
one of the significant factors for improving the accuracy of Land Surface Temperature (LST) retrieval is the correct understanding of the directional anisotropy for thermal radiance. In this paper, the multiple scattering effect between heterogeneous non-isothermal surfaces is described rigorously according to the concept of configuration factor, based on which a directional thermal radiance model is built, and the directional radiant character for urban canopy is analyzed. The model is applied to a simple urban canopy with row structure to simulate the change of Directional Brightness Temperature (DBT). The results show that the DBT is aggrandized because of the multiple scattering effects, whereas the change range of DBT is smoothed. The temperature difference, spatial distribution, emissivity of the components can all lead to the change of DBT. The “hot spot" phenomenon occurs when the proportion of high temperature component in the vision field came to a head. On the other hand, the “cool spot" phenomena occur when low temperature proportion came to the head. The “spot" effect disappears only when the proportion of every component keeps invariability. The model built in this paper can be used for the study of directional effect on emissivity, the LST retrieval over urban areas and the adjacency effect of thermal remote sensing pixels.Keywords: Directional thermal radiance, multiple scattering, configuration factor, urban canopy, hot spot effect
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 16053664 Biosecurity Control Systems in Two Phases for Poultry Farms
Authors: M. Peña Aguilar Juan, E. Nava Galván Claudia, Pastrana Palma Alberto
Abstract:
In this work was developed and implemented a thermal fogging disinfection system to counteract pathogens from poultry feces in agribusiness farms, to reduce mortality rates and increase biosafety in them. The control system consists of two phases for the conditioning of the farm during the sanitary break. In the first phase, viral and bacterial inactivation was performed by treating the stool dry cleaning, along with the development of a specialized product that foster the generation of temperatures above 55 °C in less than 24 hr, for virus inactivation. In the second phase, a process for disinfection by fogging was implemented, along with the development of a specialized disinfectant that guarantee no risk for the operators’ health or birds. As a result of this process, it was possible to minimize the level of mortality of chickens on farms from 12% to 5.49%, representing a reduction of 6.51% in the death rate, through the formula applied to the treatment of poultry litter based on oxidising agents used as antiseptics, hydrogen peroxide solutions, glacial acetic acid and EDTA in order to act on bacteria, viruses, micro bacteria and spores.
Keywords: Innovation, triple-helix, innovation, poultry farms.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 14533663 Eye Tracking: Biometric Evaluations of Instructional Materials for Improved Learning
Authors: Janet Holland
Abstract:
Eye tracking is a great way to triangulate multiple data sources for deeper, more complete knowledge of how instructional materials are really being used and emotional connections made. Using sensor based biometrics provides a detailed local analysis in real time expanding our ability to collect science based data for a more comprehensive level of understanding, not previously possible, for teaching and learning. The knowledge gained will be used to make future improvements to instructional materials, tools, and interactions. The literature has been examined and a preliminary pilot test was implemented to develop a methodology for research in Instructional Design and Technology. Eye tracking now offers the addition of objective metrics obtained from eye tracking and other biometric data collection with analysis for a fresh perspective.Keywords: Area of interest, eye tracking, biometrics, fixation, fixation count, fixation sequence, fixation time, gaze points, heat map, saccades, time to first fixation.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 8783662 Synthesis and Characterization of Nickel and Sulphur Sensitized Zinc Oxide Structures
Authors: Ella C. Linganiso, Bonex W. Mwakikunga, Trilock Singh, Sanjay Mathur, Odireleng M. Ntwaeaborwa
Abstract:
The use of nanostructured semiconducting material to catalyze degradation of environmental pollutants still receives much attention to date. One of the desired characteristics for pollutant degradation under ultra-violet visible light is the materials with extended carrier charge separation that allows for electronic transfer between the catalyst and the pollutants. In this work, zinc oxide n-type semiconductor vertically aligned structures were fabricated on silicon (100) substrates using the chemical bath deposition method. The as-synthesized structures were treated with nickel and sulphur. X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy were used to characterize the phase purity, structural dimensions and elemental composition of the obtained structures respectively. Photoluminescence emission measurements showed a decrease in both the near band edge emission as well as the defect band emission upon addition of nickel and sulphur with different concentrations. This was attributed to increased charger-carrier-separation due to the presence of Ni-S material on ZnO surface, which is linked to improved charge transfer during photocatalytic reactions.
Keywords: Carrier-charge-separation, nickel, sulphur, zinc oxide, photoluminescence.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 8563661 Creep Constitutive Equation for 2- Materials of Weldment-304L Stainless Steel
Authors: Amir Hossein Daei Sorkhabi, Farid Vakili Tahami
Abstract:
In this paper, creep constitutive equations of base (Parent) and weld materials of the weldment for cold-drawn 304L stainless steel have been obtained experimentally. For this purpose, test samples have been generated from cold drawn bars and weld material according to the ASTM standard. The creep behavior and properties have been examined for these materials by conducting uniaxial creep tests. Constant temperatures and constant load uni-axial creep tests have been carried out at two high temperatures, 680 and 720 oC, subjected to constant loads, which produce initial stresses ranging from 240 to 360 MPa. The experimental data have been used to obtain the creep constitutive parameters using numerical optimization techniques.Keywords: Creep, Constitutive equation, Cold-drawn 304L stainless steel, Weld, Base material
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 27723660 MHD Stagnation Point Flow towards a Shrinking Sheet with Suction in an Upper-Convected Maxwell (UCM) Fluid
Authors: K. Jafar, R. Nazar, A. Ishak, I. Pop
Abstract:
The present analysis considers the steady stagnation point flow and heat transfer towards a permeable shrinking sheet in an upper-convected Maxwell (UCM) electrically conducting fluid, with a constant magnetic field applied in the transverse direction to flow and a local heat generation within the boundary layer, with a heat generation rate proportional to (T-T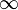 )p Using a similarity transformation, the governing system of partial differential equations is first transformed into a system of ordinary differential equations, which is then solved numerically using a finite-difference scheme known as the Keller-box method. Numerical results are obtained for the flow and thermal fields for various values of the stretching/shrinking parameter λ, the magnetic parameter M, the elastic parameter K, the Prandtl number Pr, the suction parameter s, the heat generation parameter Q, and the exponent p. The results indicate the existence of dual solutions for the shrinking sheet up to a critical value λc whose value depends on the value of M, K, and s. In the presence of internal heat absorption (Q<0) the surface heat transfer rate decreases with increasing p but increases with parameters Q and s when the sheet is either stretched or shrunk.
)p Using a similarity transformation, the governing system of partial differential equations is first transformed into a system of ordinary differential equations, which is then solved numerically using a finite-difference scheme known as the Keller-box method. Numerical results are obtained for the flow and thermal fields for various values of the stretching/shrinking parameter λ, the magnetic parameter M, the elastic parameter K, the Prandtl number Pr, the suction parameter s, the heat generation parameter Q, and the exponent p. The results indicate the existence of dual solutions for the shrinking sheet up to a critical value λc whose value depends on the value of M, K, and s. In the presence of internal heat absorption (Q<0) the surface heat transfer rate decreases with increasing p but increases with parameters Q and s when the sheet is either stretched or shrunk.
Keywords: Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD), boundary layer flow, UCM fluid, stagnation point, shrinking sheet.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 2068