Search results for: numerical investigation.
153 Investigation of Economic and Social Effects of the Dairy Cattle Support Project to Regional Economy via Cooperatives: Example of Isparta Province
Authors: Mevlüt Gül, Hilal Yılmaz, M. Göksel Akpınar, Ayse Karadağ Gürsoy, Özge Bayındır
Abstract:
Milk is a very important nutrient. Low productivity is a problem of Turkish dairy farming. During recent years, Turkish government has supported cooperatives that assist milk producers and encouraged farmers to become cooperative members. Turkish government established several ways to support specially smallholders. For example Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs (MARA) provided two to four cows to villagers on a grant or loan basis with a long repayment period at low interest rates by cooperatives. Social Support Project in Rural Areas (SSPRA) is another support program targeting only disadvantaged people, especially poor villager. Both programs have a very strong social support component and similar objectives. But there are minor differences between them in terms of target people, terms and conditions of the credit supplied Isparta province in Mediterranean region of Turkey is one of the supported regions. MARA distributed dairy cows to 1072 farmers through 16 agricultural cooperatives in Isparta province in the context of SSPRA. In this study, economic-social impacts on dairy cattle project implemented through cooperatives were examined in Isparta. Primary data were collected from 12 cooperatives- president. The data were obtained by personal interview through a questionnaire and to cooperatives and given to farms benefiting from the project in order to reveal the economic and social developments. Finding of the study revealed that project provided new job opportunities and improved quality of livestock. It was found that producers who benefited from the project were more willing to participate in cooperative or other producer organizations.Keywords: ooperative, Dairy Cattle, Economic Impact, Livestock Support Project, Social Impact.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 1864152 Material Concepts and Processing Methods for Electrical Insulation
Authors: R. Sekula
Abstract:
Epoxy composites are broadly used as an electrical insulation for the high voltage applications since only such materials can fulfill particular mechanical, thermal, and dielectric requirements. However, properties of the final product are strongly dependent on proper manufacturing process with minimized material failures, as too large shrinkage, voids and cracks. Therefore, application of proper materials (epoxy, hardener, and filler) and process parameters (mold temperature, filling time, filling velocity, initial temperature of internal parts, gelation time), as well as design and geometric parameters are essential features for final quality of the produced components. In this paper, an approach for three-dimensional modeling of all molding stages, namely filling, curing and post-curing is presented. The reactive molding simulation tool is based on a commercial CFD package, and include dedicated models describing viscosity and reaction kinetics that have been successfully implemented to simulate the reactive nature of the system with exothermic effect. Also a dedicated simulation procedure for stress and shrinkage calculations, as well as simulation results are presented in the paper. Second part of the paper is dedicated to recent developments on formulations of functional composites for electrical insulation applications, focusing on thermally conductive materials. Concepts based on filler modifications for epoxy electrical composites have been presented, including the results of the obtained properties. Finally, having in mind tough environmental regulations, in addition to current process and design aspects, an approach for product re-design has been presented focusing on replacement of epoxy material with the thermoplastic one. Such “design-for-recycling” method is one of new directions associated with development of new material and processing concepts of electrical products and brings a lot of additional research challenges. For that, one of the successful products has been presented to illustrate the presented methodology.
Keywords: Curing, epoxy insulation, numerical simulations, recycling.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 1636151 Effect of Impact Angle on Erosive Abrasive Wear of Ductile and Brittle Materials
Authors: Ergin Kosa, Ali Göksenli
Abstract:
Erosion and abrasion are wear mechanisms reducing the lifetime of machine elements like valves, pump and pipe systems. Both wear mechanisms are acting at the same time, causing a “Synergy” effect, which leads to a rapid damage of the surface. Different parameters are effective on erosive abrasive wear rate. In this study effect of particle impact angle on wear rate and wear mechanism of ductile and brittle materials was investigated. A new slurry pot was designed for experimental investigation. As abrasive particle, silica sand was used. Particle size was ranking between 200- 500 μm. All tests were carried out in a sand-water mixture of 20% concentration for four hours. Impact velocities of the particles were 4.76 m/s. As ductile material steel St 37 with Vickers Hardness Number (VHN) of 245 and quenched St 37 with 510 VHN was used as brittle material. After wear tests, morphology of the eroded surfaces were investigated for better understanding of the wear mechanisms acting at different impact angles by using Scanning Electron Microscope. The results indicated that wear rate of ductile material was higher than brittle material. Maximum wear rate was observed by ductile material at a particle impact angle of 300 and decreased further by an increase in attack angle. Maximum wear rate by brittle materials was by impact angle of 450 and decreased further up to 900. Ploughing was the dominant wear mechanism by ductile material. Microcracks on the surface were detected by ductile materials, which are nucleation centers for crater formation. Number of craters decreased and depth of craters increased by ductile materials by attack angle higher than 300. Deformation wear mechanism was observed by brittle materials. Number and depth of pits decreased by brittle materials by impact angles higher than 450. At the end it is concluded that wear rate could not be directly related to impact angle of particles due to the different reaction of ductile and brittle materials.Keywords: Erosive wear, particle impact angle, silica sand, wear rate, ductile-brittle material.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 3023150 Conceptual Design of the TransAtlantic as a Research Platform for the Development of “Green” Aircraft Technologies
Authors: Victor Maldonado
Abstract:
Recent concerns of the growing impact of aviation on climate change has prompted the emergence of a field referred to as Sustainable or “Green” Aviation dedicated to mitigating the harmful impact of aviation related CO2 emissions and noise pollution on the environment. In the current paper, a unique “green” business jet aircraft called the TransAtlantic was designed (using analytical formulation common in conceptual design) in order to show the feasibility for transatlantic passenger air travel with an aircraft weighing less than 10,000 pounds takeoff weight. Such an advance in fuel efficiency will require development and integration of advanced and emerging aerospace technologies. The TransAtlantic design is intended to serve as a research platform for the development of technologies such as active flow control. Recent advances in the field of active flow control and how this technology can be integrated on a sub-scale flight demonstrator are discussed in this paper. Flow control is a technique to modify the behavior of coherent structures in wall-bounded flows (over aerodynamic surfaces such as wings and turbine nozzles) resulting in improved aerodynamic cruise and flight control efficiency. One of the key challenges to application in manned aircraft is development of a robust high-momentum actuator that can penetrate the boundary layer flowing over aerodynamic surfaces. These deficiencies may be overcome in the current development and testing of a novel electromagnetic synthetic jet actuator which replaces piezoelectric materials as the driving diaphragm. One of the overarching goals of the TranAtlantic research platform include fostering national and international collaboration to demonstrate (in numerical and experimental models) reduced CO2/ noise pollution via development and integration of technologies and methodologies in design optimization, fluid dynamics, structures/ composites, propulsion, and controls.
Keywords: Aircraft Design, Sustainable “Green” Aviation, Active Flow Control, Aerodynamics.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 2533149 Shear Capacity of Rectangular Duct Panel Experiencing Internal Pressure
Authors: K. S. Sivakumaran, T. Thanga, B. Halabieh
Abstract:
The end panels of a large rectangular industrial duct, which experience significant internal pressures, also experience considerable transverse shear due to transfer of gravity loads to the supports. The current design practice of such thin plate panels for shear load is based on methods used for the design of plate girder webs. The structural arrangements, the loadings and the resulting behavior associated with the industrial duct end panels are, however, significantly different from those of the web of a plate girder. The large aspect ratio of the end panels gives rise to multiple bands of tension fields, whereas the plate girder web design is based on one tension field. In addition to shear, the industrial end panels are subjected to internal pressure which in turn produces significant membrane action. This paper reports a study which was undertaken to review the current industrial analysis and design methods and to propose a comprehensive method of designing industrial duct end panels for shear resistance. In this investigation, a nonlinear finite element model was developed to simulate the behavior of industrial duct end panel, along with the associated edge stiffeners, subjected to transverse shear and internal pressures. The model considered the geometric imperfections and constitutive relations for steels. Six scale independent dimensionless parameters that govern the behavior of such end panel were identified and were then used in a parametric study. It was concluded that the plate slenderness dominates the shear strength of stockier end panels, and whereas, both the plate slenderness and the aspect ratio influence the shear strength of slender end panels. Based on these studies, this paper proposes design aids for estimating the shear strength of rectangular duct end panels.Keywords: Thin plate, transverse shear, tension field, finite element analysis, parametric study, design.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 1973148 Efficiency Validation of Hybrid Cooling Application in Hot and Humid Climate Houses of KSA
Authors: Jamil Hijazi, Stirling Howieson
Abstract:
Reducing energy consumption and CO2 emissions are probably the greatest challenge now facing mankind. From considerations surrounding global warming and CO2 production, it has to be recognized that oil is a finite resource and the KSA like many other oil-rich countries will have to start to consider a horizon where hydro-carbons are not the dominant energy resource. The employment of hybrid ground-cooling pipes in combination with the black body solar collection and radiant night cooling systems may have the potential to displace a significant proportion of oil currently used to run conventional air conditioning plant. This paper presents an investigation into the viability of such hybrid systems with the specific aim of reducing cooling load and carbon emissions while providing all year-round thermal comfort in a typical Saudi Arabian urban housing block. Soil temperatures were measured in the city of Jeddah. A parametric study then was carried out by computational simulation software (DesignBuilder) that utilized the field measurements and predicted the cooling energy consumption of both a base case and an ideal scenario (typical block retro-fitted with insulation, solar shading, ground pipes integrated with hypocaust floor slabs/stack ventilation and radiant cooling pipes embed in floor). Initial simulation results suggest that careful ‘ecological design’ combined with hybrid radiant and ground pipe cooling techniques can displace air conditioning systems, producing significant cost and carbon savings (both capital and running) without appreciable deprivation of amenity.
Keywords: Cooling load, energy efficiency, ground pipe cooling, hybrid cooling strategy, hydronic radiant systems, low carbon emission, passive designs, thermal comfort.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 946147 Experimental Investigation of Visual Comfort Requirement in Garment Factories and Identify the Cost Saving Opportunities
Authors: M. A. Wijewardane, S. A. N. C. Sudasinghe, H. K. G. Punchihewa, W. K. D. L. Wickramasinghe, S. A. Philip, M. R. S. U. Kumara
Abstract:
Visual comfort is one of the major parameters that can be taken to measure the human comfort in any environment. If the provided illuminance level in a working environment does not meet the workers visual comfort, it will lead to eye-strain, fatigue, headache, stress, accidents and finally, poor productivity. However, improvements in lighting do not necessarily mean that the workplace requires more light. Unnecessarily higher illuminance levels will also cause poor visual comfort and health risks. In addition, more power consumption on lighting will also result in higher energy costs. So, during this study, visual comfort and the illuminance requirement for the workers in textile/apparel industry were studied to perform different tasks (i.e. cutting, sewing and knitting) at their workplace. Experimental studies were designed to identify the optimum illuminance requirement depending upon the varied fabric colour and type and finally, energy saving potentials due to controlled illuminance level depending on the workforce requirement were analysed. Visual performance of workers during the sewing operation was studied using the ‘landolt ring experiment’. It was revealed that around 36.3% of the workers would like to work if the illuminance level varies from 601 lux to 850 lux illuminance level and 45.9% of the workers are not happy to work if the illuminance level reduces less than 600 lux and greater than 850 lux. Moreover, more than 65% of the workers who do not satisfy with the existing illuminance levels of the production floors suggested that they have headache, eye diseases, or both diseases due to poor visual comfort. In addition, findings of the energy analysis revealed that the energy-saving potential of 5%, 10%, 24%, 8% and 16% can be anticipated for fabric colours, red, blue, yellow, black and white respectively, when the 800 lux is the prevailing illuminance level for sewing operation.
Keywords: Landolt ring experiment, lighting energy consumption, illuminance, textile and apparel industry, visual comfort.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 830146 Kinetic, Thermodynamic and Process Modeling of Synthesis of UV Curable Glyceryl and Neopentyl Glycol Acrylates
Authors: R. D. Kulkarni, Mayur Chaudhari, S. Mishra
Abstract:
Curing of paints by exposure to UV radiations is emerging as one of the best film forming technique as an alternative to traditional solvent borne oxidative and thermal curing coatings. The composition and chemistry of UV curable coatings and role of multifunctional and monofunctional monomers, oligomers, and photoinitiators have been discussed. The limitations imposed by thermodynamic equilibrium and tendency for acrylic double bond polymerizations during synthesis of multifunctional acrylates have been presented. Aim of present investigation was thus to explore the reaction variables associated with synthesis of multifunctional acrylates. Zirconium oxychloride was evaluated as catalyst against regular acid functional catalyst. The catalyzed synthesis of glyceryl acrylate and neopentyl glycol acrylate was conducted by variation of following reaction parameters: two different reactant molar ratios- 1:4 and 1:6; catalyst usage in % by moles on polyol- 2.5, 5.0 and 7.5 and two different reaction temperatures- 45 and 75 0C. The reaction was monitored by determination of acid value and hydroxy value at regular intervals, besides TLC, HPLC, and FTIR analysis of intermediates and products. On the basis of determination of reaction progress over 1-60 hrs, the esterification reaction was observed to follow 2nd order kinetics with rate constant varying from 1*10-4 to 7*10-4. The thermal and catalytic components of second order rate constant and energy of activation were also determined. Uses of these kinetic and thermodynamic parameters in design of reactor for manufacture of multifunctional acrylate ester have been presented. The synthesized multifunctional acrylates were used to formulate and apply UV curable clear coat followed by determination of curing characteristics and mechanical properties of cured film. The overall curing rates less than 05 min. were easily attained indicating economical viability of radiation curable system due to faster production schedulesKeywords: glyceryl acrylate, neopentyl glycol acrylate, kinetic modeling, zirconium oxychloride.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 2306145 An Investigation into the Social Factors that Influence Sport Participation: A Case of Gymnastics in the Western Cape
Authors: W. C. Lucas, S. Titus, M. E. M. Young
Abstract:
Gymnastics is the umbrella term that represents seven different and unique disciplines of gymnastics. Men and women of all ages and abilities practice this sport, and participation in gymnastics can develop both gross and fine motor skills, strength, flexibility, coordination and balance. There are various social factors, such as a family’s socioeconomic status or accessibility to sports facilities that may play a role in affecting levels of participation. The aim of this study is to investigate the social factors that have an influence on gymnastics participation in the Western Cape. To this end, a qualitative approach is adopted to collect data. This study also adopts the ecological systems theory as the theoretical framework, and is used to analyze and interpret current social factors that directly or indirectly influence participation in gymnastics. The study’s objectives were to ascertain which social factors hinder participation, and which social factors promote participation, thus, coaches, parents and gymnasts participated in focus group discussions. Key informant interviews took place with experts in the field of gymnastics in the Western Cape. A thematic analysis was conducted on transcriptions from the focus group discussions and key informant interviews. Social factors investigated in this study occurred in the chronosystem, macrosystem, exosystem, mesosystem, and microsystem, and had both a direct and indirect influence on the gymnast’s continued participation. These systems are defined as the environment of the individual, in which they grow and develop. The research findings of this paper are used to draw conclusions and make specific recommendations for practice and further research. The information gathered in this study can assist all stakeholders within the field of gymnastics, such as parents, judges, coaches, gymnasts, and the supporting community which surround the participating gymnast.
Keywords: Developing child, ecological systems theory, facilities, federation, gymnastics, influence, participation, social factors, socioeconomic status, sport.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 2360144 Analytical Investigation of Sediment Formation and Transport in the Vicinity of the Water Intake Structures - A Case Study of the Dez Diversion Weir in Greater Dezful
Authors: M.karavanmasjedi, N.Hedayat , A.Rohani, H.Shirin
Abstract:
Sedimentation process resulting from soil erosion in the water basin especially in arid and semi-arid where poor vegetation cover in the slope of the mountains upstream could contribute to sediment formation. The consequence of sedimentation not only makes considerable change in the morphology of the river and the hydraulic characteristics but would also have a major challenge for the operation and maintenance of the canal network which depend on water flow to meet the stakeholder-s requirements. For this reason mathematical modeling can be used to simulate the effective factors on scouring, sediment transport and their settling along the waterways. This is particularly important behind the reservoirs which enable the operators to estimate the useful life of these hydraulic structures. The aim of this paper is to simulate the sedimentation and erosion in the eastern and western water intake structures of the Dez Diversion weir using GSTARS-3 software. This is done to estimate the sedimentation and investigate the ways in which to optimize the process and minimize the operational problems. Results indicated that the at the furthest point upstream of the diversion weir, the coarser sediment grains tended to settle. The reason for this is the construction of the phantom bridge and the outstanding rocks just upstream of the structure. The construction of these along the river course has reduced the momentum energy require to push the sediment loads and make it possible for them to settle wherever the river regime allows it. Results further indicated a trend for the sediment size in such a way that as the focus of study shifts downstream the size of grains get smaller and vice versa. It was also found that the finding of the GSTARS-3 had a close proximity with the sets of the observed data. This suggests that the software is a powerful analytical tool which can be applied in the river engineering project with a minimum of costs and relatively accurate results.Keywords: Erosion, sedimentation, Dez Diversion weir, GSTARS-3
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 1618143 MHD Stagnation Point Flow towards a Shrinking Sheet with Suction in an Upper-Convected Maxwell (UCM) Fluid
Authors: K. Jafar, R. Nazar, A. Ishak, I. Pop
Abstract:
The present analysis considers the steady stagnation point flow and heat transfer towards a permeable shrinking sheet in an upper-convected Maxwell (UCM) electrically conducting fluid, with a constant magnetic field applied in the transverse direction to flow and a local heat generation within the boundary layer, with a heat generation rate proportional to (T-T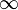 )p Using a similarity transformation, the governing system of partial differential equations is first transformed into a system of ordinary differential equations, which is then solved numerically using a finite-difference scheme known as the Keller-box method. Numerical results are obtained for the flow and thermal fields for various values of the stretching/shrinking parameter λ, the magnetic parameter M, the elastic parameter K, the Prandtl number Pr, the suction parameter s, the heat generation parameter Q, and the exponent p. The results indicate the existence of dual solutions for the shrinking sheet up to a critical value λc whose value depends on the value of M, K, and s. In the presence of internal heat absorption (Q<0) the surface heat transfer rate decreases with increasing p but increases with parameters Q and s when the sheet is either stretched or shrunk.
)p Using a similarity transformation, the governing system of partial differential equations is first transformed into a system of ordinary differential equations, which is then solved numerically using a finite-difference scheme known as the Keller-box method. Numerical results are obtained for the flow and thermal fields for various values of the stretching/shrinking parameter λ, the magnetic parameter M, the elastic parameter K, the Prandtl number Pr, the suction parameter s, the heat generation parameter Q, and the exponent p. The results indicate the existence of dual solutions for the shrinking sheet up to a critical value λc whose value depends on the value of M, K, and s. In the presence of internal heat absorption (Q<0) the surface heat transfer rate decreases with increasing p but increases with parameters Q and s when the sheet is either stretched or shrunk.
Keywords: Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD), boundary layer flow, UCM fluid, stagnation point, shrinking sheet.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 2068142 Experimental and Numerical Study of Ultra-High-Performance Fiber-Reinforced Concrete Column Subjected to Axial and Eccentric Loads
Authors: Chengfeng Fang, Mohamed Ali Sadakkathulla, Abdul Sheikh
Abstract:
Ultra-high-performance fiber reinforced concrete (UHPFRC) is a specially formulated cement-based composite characterized with an ultra-high compressive strength (fc’ = 240 MPa) and a low water-cement ratio (W/B= 0.2). With such material characteristics, UHPFRC is favored for the design and constructions of structures required high structural performance and slender geometries. Unlike conventional concrete, the structural performance of members manufactured with UHPFRC has not yet been fully studied, particularly, for UHPFRC columns with high slenderness. In this study, the behaviors of slender UHPFRC columns under concentric or eccentric load will be investigated both experimentally and numerically. Four slender UHPFRC columns were tested under eccentric loads with eccentricities, of 0 mm, 35 mm, 50 mm, and 85 mm, respectively, and one UHPFRC beam was tested under four-point bending. Finite element (FE) analysis was conducted with concrete damage plasticity (CDP) modulus to simulating the load-middle height or middle span deflection relationships and damage patterns of all UHPFRC members. Simulated results were compared against the experimental results and observation to gain the confidence of FE model, and this model was further extended to conduct parametric studies, which aim to investigate the effects of slenderness regarding failure modes and load-moment interaction relationships. Experimental results showed that the load bearing capacities of the slender columns reduced with an increase in eccentricity. Comparisons between load-middle height and middle span deflection relationships as well as damage patterns of all UHPFRC members obtained both experimentally and numerically demonstrated high accuracy of the FE simulations. Based on the available FE model, the following parametric study indicated that a further increase in the slenderness of column resulted in significant decreases in the load-bearing capacities, ductility index, and flexural bending capacities.
Keywords: Eccentric loads, ductility index, RC column, slenderness, UHPFRC.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 973141 Some Studies on Temperature Distribution Modeling of Laser Butt Welding of AISI 304 Stainless Steel Sheets
Authors: N. Siva Shanmugam, G. Buvanashekaran, K. Sankaranarayanasamy
Abstract:
In this research work, investigations are carried out on Continuous Wave (CW) Nd:YAG laser welding system after preliminary experimentation to understand the influencing parameters associated with laser welding of AISI 304. The experimental procedure involves a series of laser welding trials on AISI 304 stainless steel sheets with various combinations of process parameters like beam power, beam incident angle and beam incident angle. An industrial 2 kW CW Nd:YAG laser system, available at Welding Research Institute (WRI), BHEL Tiruchirappalli, is used for conducting the welding trials for this research. After proper tuning of laser beam, laser welding experiments are conducted on AISI 304 grade sheets to evaluate the influence of various input parameters on weld bead geometry i.e. bead width (BW) and depth of penetration (DOP). From the laser welding results, it is noticed that the beam power and welding speed are the two influencing parameters on depth and width of the bead. Three dimensional finite element simulation of high density heat source have been performed for laser welding technique using finite element code ANSYS for predicting the temperature profile of laser beam heat source on AISI 304 stainless steel sheets. The temperature dependent material properties for AISI 304 stainless steel are taken into account in the simulation, which has a great influence in computing the temperature profiles. The latent heat of fusion is considered by the thermal enthalpy of material for calculation of phase transition problem. A Gaussian distribution of heat flux using a moving heat source with a conical shape is used for analyzing the temperature profiles. Experimental and simulated values for weld bead profiles are analyzed for stainless steel material for different beam power, welding speed and beam incident angle. The results obtained from the simulation are compared with those from the experimental data and it is observed that the results of numerical analysis (FEM) are in good agreement with experimental results, with an overall percentage of error estimated to be within ±6%.
Keywords: Laser welding, Butt weld, 304 SS, FEM.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 4987140 Numerical Model of Low Cost Rubber Isolators for Masonry Housing in High Seismic Regions
Authors: Ahmad B. Habieb, Gabriele Milani, Tavio Tavio, Federico Milani
Abstract:
Housings in developing countries have often inadequate seismic protection, particularly for masonry. People choose this type of structure since the cost and application are relatively cheap. Seismic protection of masonry remains an interesting issue among researchers. In this study, we develop a low-cost seismic isolation system for masonry using fiber reinforced elastomeric isolators. The elastomer proposed consists of few layers of rubber pads and fiber lamina, making it lower in cost comparing to the conventional isolators. We present a finite element (FE) analysis to predict the behavior of the low cost rubber isolators undergoing moderate deformations. The FE model of the elastomer involves a hyperelastic material property for the rubber pad. We adopt a Yeoh hyperelasticity model and estimate its coefficients through the available experimental data. Having the shear behavior of the elastomers, we apply that isolation system onto small masonry housing. To attach the isolators on the building, we model the shear behavior of the isolation system by means of a damped nonlinear spring model. By this attempt, the FE analysis becomes computationally inexpensive. Several ground motion data are applied to observe its sensitivity. Roof acceleration and tensile damage of walls become the parameters to evaluate the performance of the isolators. In this study, a concrete damage plasticity model is used to model masonry in the nonlinear range. This tool is available in the standard package of Abaqus FE software. Finally, the results show that the low-cost isolators proposed are capable of reducing roof acceleration and damage level of masonry housing. Through this study, we are also capable of monitoring the shear deformation of isolators during seismic motion. It is useful to determine whether the isolator is applicable. According to the results, the deformations of isolators on the benchmark one story building are relatively small.Keywords: Masonry, low cost elastomeric isolator, finite element analysis, hyperelasticity, damped non-linear spring, concrete damage plasticity.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 1185139 Legal Theories Underpinning Access to Justice for Victims of Sexual Violence in Refugee Camps in Africa
Authors: O. E. Eberechi, G. P. Stevens
Abstract:
Legal theory has been referred to as the explanation of why things do or do not happen. It also describes situations and why they ensue. It provides a normative framework by which things are regulated and a foundation for the establishment of legal mechanisms/institutions that can bring about a desired change in a society. Furthermore, it offers recommendations in resolving practical problems and describes what the law is, what the law ought to be and defines the legal landscape generally. Some legal theories provide a universal standard, e.g. human rights, while others are capable of organizing and streamlining the collective use, and, by extension, bring order to society. Legal theory is used to explain how the world works and how it does not work. This paper will argue for the application of the principles of legal theory in the achievement of access to justice for female victims of sexual violence in refugee camps in Africa through the analysis of legal theories underpinning the access to justice for these women. It is a known fact that female refugees in camps in Africa often experience some form of sexual violation. The perpetrators of these incidents may never be apprehended, prosecuted, convicted or sentenced. Where prosecution does occur, the perpetrators are either acquitted as a result of poor investigation, inept prosecution, a lack of evidence, or the case may be dismissed owing to tardiness on the part of the prosecutor, which accounts for the culture of impunity in refugee camps. In other words, victims do not have access to the justice that could ameliorate the plight of the victims. There is, thus, a need for a legal framework that will facilitate access to justice for these victims. This paper will start with an introduction, and be followed by the definition of legal theory, its functions and its application in law. Secondly, it will provide a brief explanation of the problems faced by female refugees who are victims of sexual violence in refugee camps in Africa. Thirdly, it will embark on an analysis of theories which will be a help to an understanding of the precarious situation of female refugees, why they are violated, the need for access to justice for these victims, and the principles of legal theory in its usefulness in resolving access to justice for these victims.Keywords: Access to justice, underpinning legal theory, refugee, sexual violence.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 1814138 Statistical Approach to Identify Stress and Biases Impairing Decision-Making in High-Risk Industry
Authors: Ph. Fauquet-Alekhine
Abstract:
Decision-making occurs several times an hour when working in high risk industry and an erroneous choice might have undesirable outcomes for people and the environment surrounding the industrial plant. Industrial decisions are very often made in a context of acute stress. Time pressure is a crucial stressor leading decision makers sometimes to boost up the decision-making process and if it is not possible then shift to the simplest strategy. We thus found it interesting to update the characterization of the stress factors impairing decision-making at Chinon Nuclear Power Plant (France) in order to optimize decision making contexts and/or associated processes. The investigation was based on the analysis of reports addressing safety events over the last 3 years. Among 93 reports, those explicitly addressing decision-making issues were identified. Characterization of each event was undertaken in terms of three criteria: stressors, biases impairing decision making and weaknesses of the decision-making process. The statistical analysis showed that biases were distributed over 10 possibilities among which the hypothesis confirmation bias was clearly salient. No significant correlation was found between criteria. The analysis indicated that the main stressor was time pressure and highlights an unexpected form of stressor: the trust asymmetry principle of the expert. The analysis led to the conclusion that this stressor impaired decision-making from a psychological angle rather than from a physiological angle: it induces defensive bias of self-esteem, self-protection associated with a bias of confirmation. This leads to the hypothesis that this stressor can intervene in some cases without being detected, and to the hypothesis that other stressors of the same kind might occur without being detected too. Further investigations addressing these hypotheses are considered. The analysis also led to the conclusion that dealing with these issues implied i) decision-making methods being well known to the workers and automated and ii) the decision-making tools being well known and strictly applied. Training was thus adjusted.
Keywords: Bias, expert, high risk industry, stress.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 667137 Computational Assistance of the Research, Using Dynamic Vector Logistics of Processes for Critical Infrastructure Subjects Continuity
Authors: J. Urbánek Jiří, Krahulec Josef, Johanidesová Jitka, F. Urbánek Jiří
Abstract:
This paper deals with using of prevailing operation system MS Office (SmartArt...) for mathematical models, using DYVELOP (Dynamic Vector Logistics of Processes) method. It serves for crisis situations investigation and modelling within the organizations of critical infrastructure. In first part of paper, it will be introduced entities, operators, and actors of DYVELOP method. It uses just three operators of Boolean algebra and four types of the entities: the Environments, the Process Systems, the Cases, and the Controlling. The Process Systems (PrS) have five “brothers”: Management PrS, Transformation PrS, Logistic PrS, Event PrS and Operation PrS. The Cases have three “sisters”: Process Cell Case, Use Case, and Activity Case. They all need for the controlling of their functions special Ctrl actors, except ENV – it can do without Ctrl. Model´s maps are named the Blazons and they are able mathematically - graphically express the relationships among entities, actors and processes. In second part of this paper, the rich blazons of DYVELOP method will be used for the discovering and modelling of the cycling cases and their phases. The blazons need live PowerPoint presentation for better comprehension of this paper mission. The crisis management of energetic crisis infrastructure organization is obliged to use the cycles for successful coping of crisis situations. Several times cycling of these cases is necessary condition for the encompassment for both emergency events and the mitigation of organization´s damages. Uninterrupted and continuous cycling process brings for crisis management fruitfulness and it is good indicator and controlling actor of organizational continuity and its sustainable development advanced possibilities. The research reliable rules are derived for the safety and reliable continuity of energetic critical infrastructure organization in the crisis situation.Keywords: Blazons, computational assistance, DYVELOP method, critical infrastructure.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 1634136 The Study of Cost Accounting in S Company Based On TDABC
Authors: Heng Ma
Abstract:
Third-party warehousing logistics has an important role in the development of external logistics. At present, the third-party logistics in our country is still a new industry, the accounting system has not yet been established, the current financial accounting system of third-party warehousing logistics is mainly in the traditional way of thinking, and only able to provide the total cost information of the entire enterprise during the accounting period, unable to reflect operating indirect cost information. In order to solve the problem of third-party logistics industry cost information distortion, improve the level of logistics cost management, the paper combines theoretical research and case analysis method to reflect cost allocation by building third-party logistics costing model using Time-Driven Activity-Based Costing(TDABC), and takes S company as an example to account and control the warehousing logistics cost.Based on the idea of “Products consume activities and activities consume resources”, TDABC put time into the main cost driver and use time-consuming equation resources assigned to cost objects. In S company, the objects focuses on three warehouse, engaged with warehousing and transportation (the second warehouse, transport point) service. These three warehouse respectively including five departments, Business Unit, Production Unit, Settlement Center, Security Department and Equipment Division, the activities in these departments are classified by in-out of storage forecast, in-out of storage or transit and safekeeping work. By computing capacity cost rate, building the time-consuming equation, the paper calculates the final operation cost so as to reveal the real cost.The numerical analysis results show that the TDABC can accurately reflect the cost allocation of service customers and reveal the spare capacity cost of resource center, verifies the feasibility and validity of TDABC in third-party logistics industry cost accounting. It inspires enterprises focus on customer relationship management and reduces idle cost to strengthen the cost management of third-party logistics enterprises.
Keywords: Third-party logistics enterprises, TDABC, cost management, S company.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 2435135 Investigation into the Optimum Hydraulic Loading Rate for Selected Filter Media Packed in a Continuous Upflow Filter
Authors: A. Alzeyadi, E. Loffill, R. Alkhaddar
Abstract:
Continuous upflow filters can combine the nutrient (nitrogen and phosphate) and suspended solid removal in one unit process. The contaminant removal could be achieved chemically or biologically; in both processes the filter removal efficiency depends on the interaction between the packed filter media and the influent. In this paper a residence time distribution (RTD) study was carried out to understand and compare the transfer behaviour of contaminants through a selected filter media packed in a laboratory-scale continuous up flow filter; the selected filter media are limestone and white dolomite. The experimental work was conducted by injecting a tracer (red drain dye tracer –RDD) into the filtration system and then measuring the tracer concentration at the outflow as a function of time; the tracer injection was applied at hydraulic loading rates (HLRs) (3.8 to 15.2 m h-1). The results were analysed according to the cumulative distribution function F(t) to estimate the residence time of the tracer molecules inside the filter media. The mean residence time (MRT) and variance σ2 are two moments of RTD that were calculated to compare the RTD characteristics of limestone with white dolomite. The results showed that the exit-age distribution of the tracer looks better at HLRs (3.8 to 7.6 m h-1) and (3.8 m h-1) for limestone and white dolomite respectively. At these HLRs the cumulative distribution function F(t) revealed that the residence time of the tracer inside the limestone was longer than in the white dolomite; whereas all the tracer took 8 minutes to leave the white dolomite at 3.8 m h-1. On the other hand, the same amount of the tracer took 10 minutes to leave the limestone at the same HLR. In conclusion, the determination of the optimal level of hydraulic loading rate, which achieved the better influent distribution over the filtration system, helps to identify the applicability of the material as filter media. Further work will be applied to examine the efficiency of the limestone and white dolomite for phosphate removal by pumping a phosphate solution into the filter at HLRs (3.8 to 7.6 m h-1).Keywords: Filter media, hydraulic loading rate, residence time distribution, tracer.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 1871134 Isolation and Probiotic Characterization of Arsenic-Resistant Lactic Acid Bacteria for Uptaking Arsenic
Authors: Jatindra N. Bhakta, Kouhei Ohnishi, Yukihiro Munekage, Kozo Iwasaki
Abstract:
The growing health hazardous impact of arsenic (As) contamination in environment is the impetus of the present investigation. Application of lactic acid bacteria (LAB) for the removal of toxic and heavy metals from water has been reported. This study was performed in order to isolate and characterize the Asresistant LAB from mud and sludge samples for using as efficient As uptaking probiotic. Isolation of As-resistant LAB colonies was performed by spread plate technique using bromocresol purple impregnated-MRS (BP-MRS) agar media provided with As @ 50 μg/ml. Isolated LAB were employed for probiotic characterization process, acid and bile tolerance, lactic acid production, antibacterial activity and antibiotic tolerance assays. After As-resistant and removal characterizations, the LAB were identified using 16S rDNA sequencing. A total of 103 isolates were identified as As-resistant strains of LAB. The survival of 6 strains (As99-1, As100-2, As101-3, As102-4, As105-7, and As112-9) was found after passing through the sequential probiotic characterizations. Resistant pattern pronounced hollow zones at As concentration >2000 μg/ml in As99-1, As100-2, and As101-3 LAB strains, whereas it was found at ~1000 μg/ml in rest 3 strains. Among 6 strains, the As uptake efficiency of As102-4 (0.006 μg/h/mg wet weight of cell) was higher (17 – 209%) compared to remaining LAB. 16S rDNA sequencing data of 3 (As99- 1, As100-2, and As101-3) and 3 (As102-4, As105-7, and As112-9) LAB strains clearly showed 97 to 99% (340 bp) homology to Pediococcus dextrinicus and Pediococcus acidilactici, respectively. Though, there was no correlation between the metal resistant and removal efficiency of LAB examined but identified elevated As removing LAB would probably be a potential As uptaking probiotic agent. Since present experiment concerned with only As removal from pure water, As removal and removal mechanism in natural condition of intestinal milieu should be assessed in future studies.Keywords: Lactic acid bacteria, As-resistant, characterization, Pediococcus sp., As removal probiotic.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 2734133 Monte Carlo and Biophysics Analysis in a Criminal Trial
Authors: Luca Indovina, Carmela Coppola, Carlo Altucci, Riccardo Barberi, Rocco Romano
Abstract:
In this paper a real court case, held in Italy at the Court of Nola, in which a correct physical description, conducted with both a Monte Carlo and biophysical analysis, would have been sufficient to arrive at conclusions confirmed by documentary evidence, is considered. This will be an example of how forensic physics can be useful in confirming documentary evidence in order to reach hardly questionable conclusions. This was a libel trial in which the defendant, Mr. DS (Defendant for Slander), had falsely accused one of his neighbors, Mr. OP (Offended Person), of having caused him some damages. The damages would have been caused by an external plaster piece that would have detached from the neighbor’s property and would have hit Mr DS while he was in his garden, much more than a meter far away from the facade of the building from which the plaster piece would have detached. In the trial, Mr. DS claimed to have suffered a scratch on his forehead, but he never showed the plaster that had hit him, nor was able to tell from where the plaster would have arrived. Furthermore, Mr. DS presented a medical certificate with a diagnosis of contusion of the cerebral cortex. On the contrary, the images of Mr. OP’s security cameras do not show any movement in the garden of Mr. DS in a long interval of time (about 2 hours) around the time of the alleged accident, nor do they show any people entering or coming out from the house of Mr. DS in the same interval of time. Biophysical analysis shows that both the diagnosis of the medical certificate and the wound declared by the defendant, already in conflict with each other, are not compatible with the fall of external plaster pieces too small to be found. The wind was at a level 1 of the Beaufort scale, that is, unable to raise even dust (level 4 of the Beaufort scale). Therefore, the motion of the plaster pieces can be described as a projectile motion, whereas collisions with the building cornice can be treated using Newtons law of coefficients of restitution. Numerous numerical Monte Carlo simulations show that the pieces of plaster would not have been able to reach even the garden of Mr. DS, let alone a distance over 1.30 meters. Results agree with the documentary evidence (images of Mr. OP’s security cameras) that Mr. DS could not have been hit by plaster pieces coming from Mr. OP’s property.Keywords: Biophysical analysis, Monte Carlo simulations, Newton’s law of restitution, projectile motion.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 614132 Effect of Acid Rain on Vigna radiata
Authors: Nilima Gajbhiye
Abstract:
The acid rain causes change in pH level of soil it is directly influence on root and leaf growth. Yield of the crop was reduced if acidity of soil is more. Acid rain seeps into the earth and poisons plants and trees by dissolving toxic substances in the soil, such as aluminum, which get absorbed by the roots. In present investigation, effect of acid rain on crop Vigna radiata was studied. The effect of acid rain on change in soil fertility was detected in which pH of control sample was 6.5 and pH of 1% H2SO4 and 1% HNO3 were 3.5. Nitrogen nitrate in soil was high in 1% HNO3 treated soil & Control sample. Ammonium nitrogen in soil was low in 1% HNO3 & H2SO4 treated soil. Ammonium nitrogen was medium in control and other samples. The effect of acid rain on seed germination on 3rd day of germination control sample growth was 6.1cm with plumule 0.001% HNO3 & 0.001% H2SO4 was 5.5cm with plumule and 8cm with plumule. On 10th day fungal growth was observed in 1% and 0.1% H2SO4 concentrations when all plants were dead. The effect of acid rain on crop productivity was investigated on 3rd day roots were developed in plants. On 12th day Vigna radiata showed more growth in 0.1% HNO3 and 0.1% H2SO4 treated plants as compare to control plants. On 20th day development of discoloration of plant pigments were observed on acid treated plants leaves. On 34th day Vigna radiata showed flower in 0.1% HNO3, 0.01% HNO3 and 0.01% H2SO4treated plants and no flowers were observed on control plants. On 42th day 0.1% HNO3, 0.01% HNO and 0.01% H2SO4 treated Vigna radiata variety and control plants were showed seeds on plants. In Vigna radiate variety 0.1%, 0.01% HNO3, 0.01% H2SO4treated plants were dead on 46th day and fungal growth was observed. The toxicological study was carried out on Vigna radiata plants exposed to 1% HNO3 cells were damaged more than 1% H2SO4. Leaf sections exposed to 0.001% HNO3 & H2SO4 showed less damaged of cells and pigmentation observed in entire slide when compare with control plant.
Keywords: Acid rain, pH, Vigna radiate, HNO3 & H2SO4.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 3263131 Research of the Load Bearing Capacity of Inserts Embedded in CFRP under Different Loading Conditions
Authors: F. Pottmeyer, M. Weispfenning, K. A. Weidenmann
Abstract:
Continuous carbon fiber reinforced plastics (CFRP) exhibit a high application potential for lightweight structures due to their outstanding specific mechanical properties. Embedded metal elements, so-called inserts, can be used to join structural CFRP parts. Drilling of the components to be joined can be avoided using inserts. In consequence, no bearing stress is anticipated. This is a distinctive benefit of embedded inserts, since continuous CFRP have low shear and bearing strength. This paper aims at the investigation of the load bearing capacity after preinduced damages from impact tests and thermal-cycling. In addition, characterization of mechanical properties during dynamic high speed pull-out testing under different loading velocities was conducted. It has been shown that the load bearing capacity increases up to 100% for very high velocities (15 m/s) in comparison with quasi-static loading conditions (1.5 mm/min). Residual strength measurements identified the influence of thermal loading and preinduced mechanical damage. For both, the residual strength was evaluated afterwards by quasi-static pull-out tests. Taking into account the DIN EN 6038 a high decrease of force occurs at impact energy of 16 J with significant damage of the laminate. Lower impact energies of 6 J, 9 J, and 12 J do not decrease the measured residual strength, although the laminate is visibly damaged - distinguished by cracks on the rear side. To evaluate the influence of thermal loading, the specimens were placed in a climate chamber and were exposed to various numbers of temperature cycles. One cycle took 1.5 hours from -40 °C to +80 °C. It could be shown that already 10 temperature cycles decrease the load bearing capacity up to 20%. Further reduction of the residual strength with increasing number of thermal cycles was not observed. Thus, it implies that the maximum damage of the composite is already induced after 10 temperature cycles.
Keywords: Composite, joining, inserts, dynamic loading, thermal loading, residual strength, impact.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 1828130 The Study of Using Mon Dance in Pathum Thani Province’s Tradition
Authors: Dusittorn Ngamying
Abstract:
This investigation is focused on using of Mon dance in Pathum Thani Province’s tradition and has the following objectives: 1) to study the background of Mon dance in Pathum Thani Province; 2) to study Mon dance in Pathum Thani Province; and 3) to study of using Mon dance in Pathum Thani province’s tradition. This qualitative research was conducted in Pathum Thani province (in the central of Thailand). Data was collected from documentary study and field data by means of observation, interview, and group discussion. Workshops were also held with a total of 100 attendees, comprised of 20 key informants, 40 casual informants and 40 general informants. Data was validated using the triangulation technique and the findings are presented using the descriptive analysis. The results of the study show that the historical background of Mon dance in Pathum Thani Province initiated during the war evacuation from Martaban (south of Burma) to settle down in Sam Khok, Pathum Thani Province in Ayutthaya period to Rattanakosin. The study found that Mon dance typically consists of 12-13 dancing process. The melodies have 12-13 songs. Piphat Mon (Mon traditional music ensemble) is used in the performance. Performers are dressed in Mon traditional costumes. The performers are 6-12 women and depending on the employer’s demands. Length of the performance varies from the duration of music orchestration. Rituals and customs performed are paying homage to teachers before the performance. The offerings are composed of flowers, incense sticks, candles, money gifts which are well arranged on a tray with pedestal, and also liquors, tobaccos and pure water for asking propitiousness. For the use of Mon dance in Pathum Thani Province’s tradition, it is found that the dance is commonly performed in the funeral ceremonial tradition at present because the physical postures of the performance are considered graceful and exquisite. In addition, as for its value, it has long been believed since the ancient times that Mon dance was a sacred thing considered as the dignity and glorification especially for funeral ceremonies of priest or royal hierarchy classes. However, Mon dance has continued to be used in the traditions associated with Mon people activities in Pathum Thani Province for instance customary welcome for honor guest and Songkran festival.Keywords: Mon dance, traditions, Pathum Thani Province.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 1497129 Crossover Memories and Code-Switching in the Narratives of Arabic-Hebrew and Hebrew-English Bilingual Adults in Israel
Authors: Amani Jaber-Awida
Abstract:
This study examines two bilingual phenomena in the narratives of Arabic Hebrew and Hebrew-English bilingual adults in Israel: CO memories and code-switching (CS). The study examined these phenomena in the context of autobiographical memory, using a cue word technique. Student experimenters held two sessions in the homes of the participants. In separate language sessions, the participant was asked to look first at each of 16 cue words and then to state a concrete memory. After stating the memory, participants reported whether their memories were in the same language of the experiment session or different. Memories were classified as ‘Crossovers’ (CO) or ‘Same Language’ (SL) according to participants' self-reports. Participants were also required to elaborate about the setting, interlocutors and other languages involved in the specific memory. Beyond replicating the procedure of cuing technique, one memory from a specific lifespan period was chosen per participant, and the participant was required to provide further details about it. For the more detailed memories, CS count was conducted. Both bilingual groups confirmed the Reminiscence Bump phenomenon, retrieving more memories in the 10-30 age period. CO memories prevailed in second language sessions (L2). Same language memories were more abundant in first language sessions (L1). Higher CS frequency was found in L2 sessions. Finally, as predicted, 'individual' CS was prevalent in L2 sessions, but 'community-based' CS was not higher in L1 sessions. The two bilingual measures in this study, crossovers, and CS came from different research traditions, the former from an experimental paradigm in the psychology of autobiographical memory based on self-reported judgments, the latter a behavioral measure from linguistics. This merger of approaches offers new insight into the field of bilingual autobiographical memory. In addition, the study attempted to shed light on the investigation of motivations for CS, beginning with Walters’ SPPL Model and concluding with a distinction between ‘community-based’ and individual motivations.
Keywords: Autobiographical memory, code-switching, crossover memories, reminiscence bump.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 785128 The Effect of Multiple Environmental Conditions on Acacia Senegal Seedling’s Carbon, Nitrogen, and Hydrogen Contents: An Experimental Investigation
Authors: Abdoelmoniem A. Attaelmanan, Ahmed A. H. Siddig
Abstract:
This study was conducted in light of continual global climate changes that projected increasing aridity, changes in soil fertility, and pollution. Plant growth and development largely depend on the combination of availing water and nutrients in the soil. Changes in the climate and atmospheric chemistry can cause serious effects on these growth factors. Plant carbon (C), nitrogen (N), and hydrogen (H) play a fundamental role in the maintenance of ecosystem structure and function. Hashab (Acacia senegal), which produces gum Arabic, supports dryland ecosystems in tropical zones by its potentiality to restore degraded soils; hence, it is ecologically and economically important for the dry areas of sub-Saharan Africa. The study aims at investigating the effects of water stress (simulated drought) and poor soil type on Acacia senegal C, N, and H contents. Seven-day-old seedlings were assigned to the treatments in split-plot design for four weeks. The main plot is irrigation interval (well-watered and water-stressed), and the subplot is soil types (silt and sandy soils). Seedling's C%, N%, and H% were measured using CHNS-O Analyzer and applying Standard Test Method. Irrigation intervals and soil types had no effects on seedlings and leaves C%, N%, and H%, irrigation interval had affected stem C% and H%, both irrigation intervals and soil types had affected root N% and interaction effect of water and soil was found on leaves and root's N%. Application of well-watered irrigation with soil that is rich in N and other nutrients would result in the greatest seedling C, N, and H content which will enhance growth and biomass accumulation and can play a crucial role in ecosystem productivity and services in the dryland regions.
Keywords: Acacia senegal, Africa, climate change, drylands, nutrients biomass, Sub-Sahara, Sudan.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 533127 Hydrogen and Diesel Combustion on a Single Cylinder Four Stroke Diesel Engine in Dual Fuel mode with Varying Injection Strategies
Authors: Probir Kumar Bose, Rahul Banerjee, Madhujit Deb
Abstract:
The present energy situation and the concerns about global warming has stimulated active research interest in non-petroleum, carbon free compounds and non-polluting fuels, particularly for transportation, power generation, and agricultural sectors. Environmental concerns and limited amount of petroleum fuels have caused interests in the development of alternative fuels for internal combustion (IC) engines. The petroleum crude reserves however, are declining and consumption of transport fuels particularly in the developing countries is increasing at high rates. Severe shortage of liquid fuels derived from petroleum may be faced in the second half of this century. Recently more and more stringent environmental regulations being enacted in the USA and Europe have led to the research and development activities on clean alternative fuels. Among the gaseous fuels hydrogen is considered to be one of the clean alternative fuel. Hydrogen is an interesting candidate for future internal combustion engine based power trains. In this experimental investigation, the performance and combustion analysis were carried out on a direct injection (DI) diesel engine using hydrogen with diesel following the TMI(Time Manifold Injection) technique at different injection timings of 10 degree,45 degree and 80 degree ATDC using an electronic control unit (ECU) and injection durations were controlled. Further, the tests have been carried out at a constant speed of 1500rpm at different load conditions and it can be observed that brake thermal efficiency increases with increase in load conditions with a maximum gain of 15% at full load conditions during all injection strategies of hydrogen. It was also observed that with the increase in hydrogen energy share BSEC started reducing and it reduced to a maximum of 9% as compared to baseline diesel at 10deg ATDC injection during maximum injection proving the exceptional combustion properties of hydrogen.Keywords: Hydrogen, performance, combustion, alternative fuels.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 3412126 Juxtaposition of the Past and the Present: A Pragmatic Stylistic Analysis of the Short Story “Too Much Happiness” by Alice Munro
Authors: Inas Hussein
Abstract:
Alice Munro is a Canadian short-story writer who has been regarded as one of the greatest writers of fiction. Owing to her great contribution to fiction, she was the first Canadian woman and the only short-story writer ever to be rewarded the Nobel Prize for Literature in 2013. Her literary works include collections of short stories and one book published as a novel. Her stories concentrate on the human condition and the human relationships as seen through the lens of daily life. The setting in most of her stories is her native Canada- small towns much similar to the one where she grew up. Her writing style is not only realistic but is also characterized by autobiographical, historical and regional features. The aim of this research is to analyze one of the key stylistic devices often adopted by Munro in her fictions: the juxtaposition of the past and the present, with reference to the title story in Munro's short story collection Too Much Happiness. The story under exploration is a brief biography of the Russian Mathematician and novelist Sophia Kovalevsky (1850 – 1891), the first woman to be appointed as a professor of Mathematics at a European University in Stockholm. Thus, the story has a historical protagonist and is set on the European continent. Munro dramatizes the severe historical and cultural constraints that hindered the career of the protagonist. A pragmatic stylistic framework is being adopted and the qualitative analysis is supported by textual reference. The stylistic analysis reveals that the juxtaposition of the past and the present is one of the distinctive features that characterize the author; in a typical Munrovian manner, the protagonist often moves between the units of time: the past, the present and, sometimes, the future. Munro's style is simple and direct but cleverly constructed and densely complicated by the presence of deeper layers and stories within the story. Findings of the research reveal that the story under investigation merits reading and analyzing. It is recommended that this story and other stories by Munro are analyzed to further explore the features of her art and style.
Keywords: Alice Munro, Too Much Happiness, juxtaposition of past and present, pragmatic stylistics.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 1029125 Forensic Medical Capacities of Research of Saliva Stains on Physical Evidence after Washing
Authors: Saule Mussabekova
Abstract:
Recent advances in genetics have allowed increasing acutely the capacities of the formation of reliable evidence in conducting forensic examinations. Thus, traces of biological origin are important sources of information about a crime. Currently, around the world, sexual offenses have increased, and among them are those in which the criminals use various detergents to remove traces of their crime. A feature of modern synthetic detergents is the presence of biological additives - enzymes. Enzymes purposefully destroy stains of biological origin. To study the nature and extent of the impact of modern washing powders on saliva stains on the physical evidence, specially prepared test specimens of different types of tissues to which saliva was applied have been examined. Materials and Methods: Washing machines of famous manufacturers of household appliances have been used with different production characteristics and advertised brands of washing powder for test washing. Over 3,500 experimental samples were tested. After washing, the traces of saliva were identified using modern research methods of forensic medicine. Results: The influence was tested and the dependence of the use of different washing programs, types of washing machines and washing powders in the process of establishing saliva trace and identify of the stains on the physical evidence while washing was revealed. The results of experimental and practical expert studies have shown that in most cases it is not possible to draw the conclusions in the identification of saliva traces on physical evidence after washing. This is a consequence of the effect of biological additives and other additional factors on traces of saliva during washing. Conclusions: On the basis of the results of the study, the feasibility of saliva traces of the stains on physical evidence after washing is established. The use of modern molecular genetic methods makes it possible to partially solve the problems arising in the study of unlaundered evidence. Additional study of physical evidence after washing facilitates detection and investigation of sexual offenses against women and children.
Keywords: Saliva research, modern synthetic detergents, laundry detergents, forensic medicine.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 1317124 Fatal Road Accident Causer's Driving Aptitude in Hungary
Authors: A. Juhász, M. Fogarasi
Abstract:
Those causing fatal traffic accidents are traumatized, which negatively influences their cognitive functions and their personality. In order to clarify how much the trauma of causing a fatal accident effects their driving skills and personality traits, the results of a psychological aptitude and a personality test of drivers carelessly causing fatal accidents and of drivers not causing any accidents were compared separately. The sample (N = 354) consists of randomly selected drivers from the Transportation Aptitude and Examination Centre database who caused fatal accidents (Fatal group, n = 177) or did not cause accidents (Control group, n = 177). The aptitude tests were taken between 2014 and 2019. The comparison of the 2 groups was done according to 3 aspects: 1. Categories of aptitude (suitable, restricted, unsuited); 2. Categories of causes (ability, personality, ability and personality) within the restricted or unsuited (altogether: non-suitable subgroups); 3. Categories of ability and personality within the non-suitable subgroups regardless of the cause-category. Within ability deficiency, the two groups include those, whose ability factor is impaired or limited. This is also true in case of personality failure. Compared to the control group, the number of restricted drivers causing fatal accidents is significantly higher (p < .000) and the number of unsuited drivers is higher on a tendency-level (p = .06). Compared to the control group in the fatal non-suitable subgroup, the ratio of restricted suitability and the unsuitability due to ability factors is exclusively significantly lower (p < .000). The restricted suitability and the unsuitability due to personality factors are more significant in the fatal non-suitable subgroup (p < .000). Incapacity due to combination of ability and personality is also significantly higher in the fatal group (p = .002). Compared to the control group both ability and personality factors are also significantly higher in the fatal non-suitable subgroup (p < .000). Overall, the control group is more eligible for driving than drivers who have caused fatalities. The ability and personality factors are significantly higher in the case of fatal accident causers who are non-suitable for driving. Moreover the concomitance of ability and personality factors occur almost exclusively to drivers who caused fatal accidents. Further investigation is needed to understand the causes and how the aptitude test results for the fatal group could improve over time.
Keywords: Aptitude, unsuited, fatal accident, ability, personality.
Procedia APA BibTeX Chicago EndNote Harvard JSON MLA RIS XML ISO 690 PDF Downloads 688